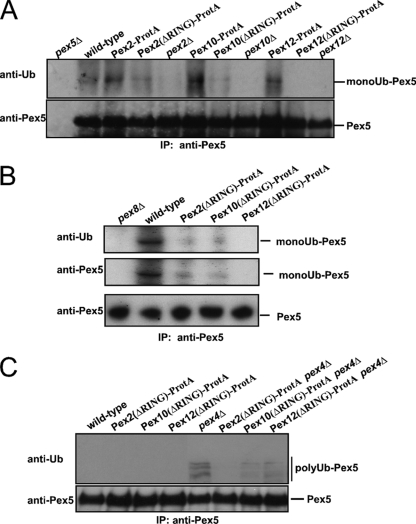
FIG. 7.
Pex12-RING is required for Pex5 monoubiquitination while Pex2-RING is essential for Pex5 polyubiquitination. The influence of genomic truncations on the monoubiquitination (A and B) and polyubiquitination (C) of Pex5 was analyzed in vivo. Pex5 was isolated by immunoprecipitation from total cell membranes prepared from the indicated oleic acid-induced wild-type strains, null mutants, or strains harboring the genomic truncation of the RING peroxins. The pex8Δ strain served as a negative control. Samples were analyzed by immunoblot analysis with antibodies against Pex5 and Ub. (A and B) To monitor monoubiquitination, NEM was applied to the cells prior to breakage. Genomic truncation of the Pex12-RING prevents the receptor monoubiquitination whereas this modification is still present upon truncation of either the RING domain of Pex2 or that of Pex10. This result indicates that Pex12 is responsible for the Pex5 monoubiquitination. (C) Polyubiquitination occurs in mutants affected in late stages of the peroxisomal protein import pathway represented here by the pex4Δ strain. Truncation of the RING domain of Pex2 but not of Pex10 or Pex12 prevents the receptor polyubiquitination in a pex4Δ background. This result demonstrates that the RING domain of Pex2 is required for Pex5 polyubiquitination.