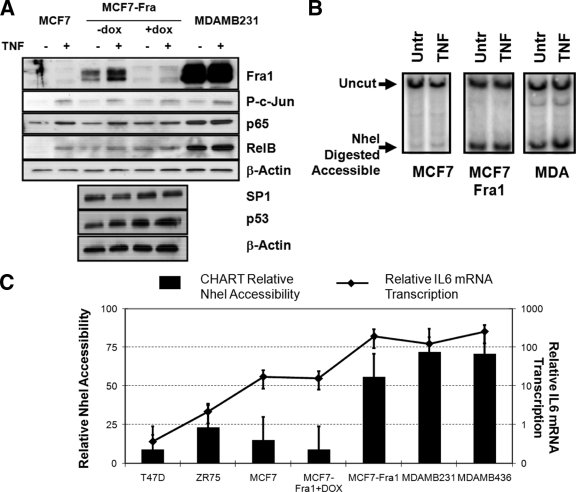
FIG. 9.
Increased Fra1 expression levels increase chromatin accessibility and gene expression across the IL-6 gene promoter. MCF7, MCF7-Fra1, doxycycline (dox)-cultured MCF-Fra-1, MDA-MB231, MDA-MB468, T47D, and ZR75 cells were left untreated (Untr) or were treated for 3 h with TNF (2,500 IU/ml) as indicated in panels A to C. (A) Total cell extracts were analyzed by Western analysis for the presence of AP-1 Fra-1, (P)-c-Jun, NF-κB p65 and RelB, Sp1, p53, and β-actin expression as indicated. (B) Chromatin DNA, isolated from different cell types left untreated or treated with doxycycline for 24 h and/or TNF for 3 h as indicated, was exposed to NheI restriction enzyme. NheI-accessible chromatin fragments which are digested were revealed by restriction IEL with the HindIII-PstI probe for the samples indicated. (C) Chromatin DNA, isolated from various cell types left untreated or treated with doxycycline for 24 h as indicated, was exposed to NheI restriction enzyme. NheI-unaccessible chromatin fragments which remain undigested were quantified by CHART qPCR and subtracted from CHART qPCR amounts obtained with intact undigested chromatin DNA to yield the percent NheI chromatin accessibility (as accessible plus unaccessible fractions add up to 100%). Corresponding IL-6 mRNA transcription levels of the various cell types left untreated or treated with doxycycline for 24 h were quantified by qPCR and are indicated as the line graph in panel C (right axis).