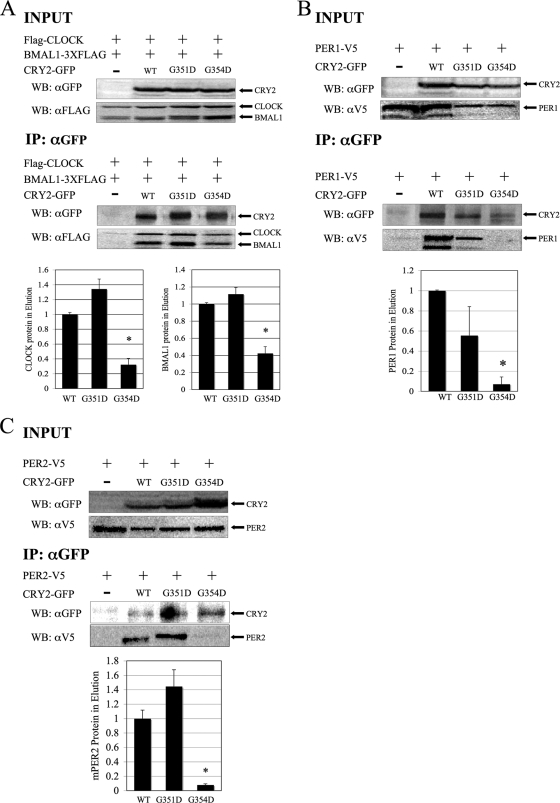
FIG. 5.
CRY2G354D exhibits decreased binding to CLOCK-BMAL1, PER1, and PER2, while CRY2G354D retains strong binding. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation. HEK293 cells were transfected with Flag-Clock, Bmal1-Flag3 (3XFLAG), and Cry2-GFP constructs, as indicated. CRY2 proteins were immunoprecipitated, using anti-GFP in conjunction with a protein G IP kit. Copurified proteins were detected by Western blotting (WB) using rabbit anti-GFP (αGFP) or monoclonal mouse anti-FLAG M2 (αFLAG) antibodies. The images shown are representative of three independent experiments. Underneath, the quantitation of the eluted samples from coimmunoprecipitation is shown. The ratio of CRY2 to CLOCK or CRY2 to BMAL1 in the elution was calculated. The data were normalized such that the average amount of CLOCK and BMAL1 that wild-type CRY2 pulled down was set to 1. The error bars represent the SEM. The asterisks indicate groups that were significantly different from each other (P < 0.05). (B and C) Coimmunoprecipitation of CRY2 mutants with PER proteins. In this experiment, HEK293 cells were transfected with PER1-V5 (B) or PER2-V5 (C) and CRY2-GFP constructs, as indicated. Wild-type and mutant CRY2 proteins were pulled down, as described above. Copurified proteins were detected by Western blotting, using either rabbit anti-GFP or monoclonal mouse anti-V5 antibodies. The images shown are representative of three independent experiments.