Figure 1.
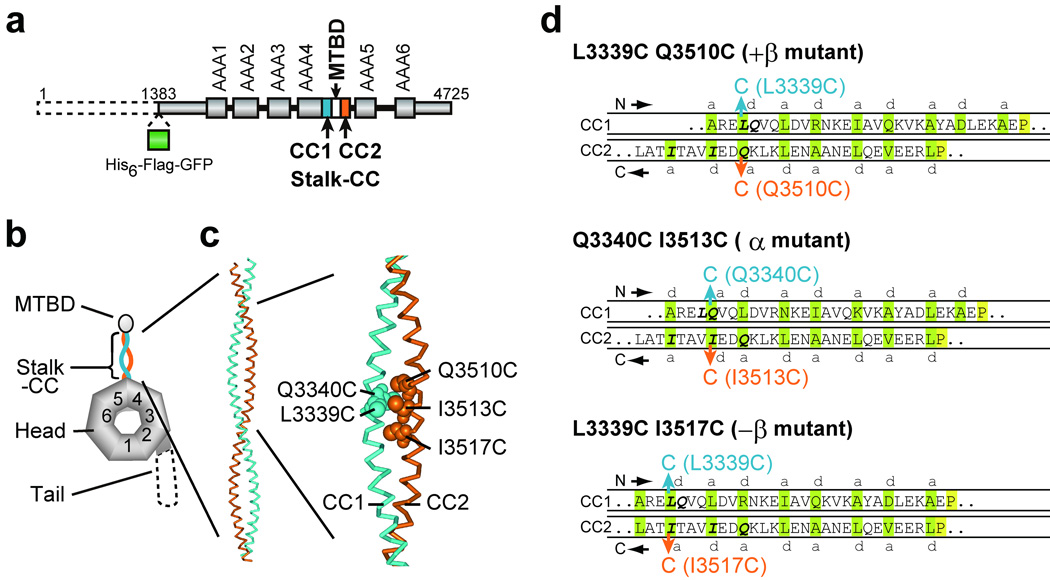
Design of double-Cys mutants of the 380-kDa dynein motor domain for disulfide cross-linking between the two helices of the stalk coiled coil. (a) Domain organization and (b) predicted domain structure of the D. discoideum cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain. The dashed line represents the region deleted in the 380-kDa motor domain. (c) A homology-based structural model of the stalk coiled coil in the α registry (PDB id: 2bot26; numbered as in the D. discoideum dynein heavy chain) with Cys substitutions at L3339, Q3340, Q3510, I3513, and I3517 indicated by CPK representations. (d) Diagrams of the distal one-third portion of the stalk coiled coil that show expected alignments between the two helices in cross-linked double-Cys mutants. The introduced Cys pairs for disulfide bond formation are colored blue and orange. Amino acids predicted to occupy a and d positions of the heptad repeats 26 are shaded green. The absolutely conserved P3366 and P3491 residues, close to the boundary between the stalk and MTBD44, are shaded yellow. The +β, α, and −β registries correspond to the 26:19, 22:19, and 19:19 configurations, respectively, in ref. 26.