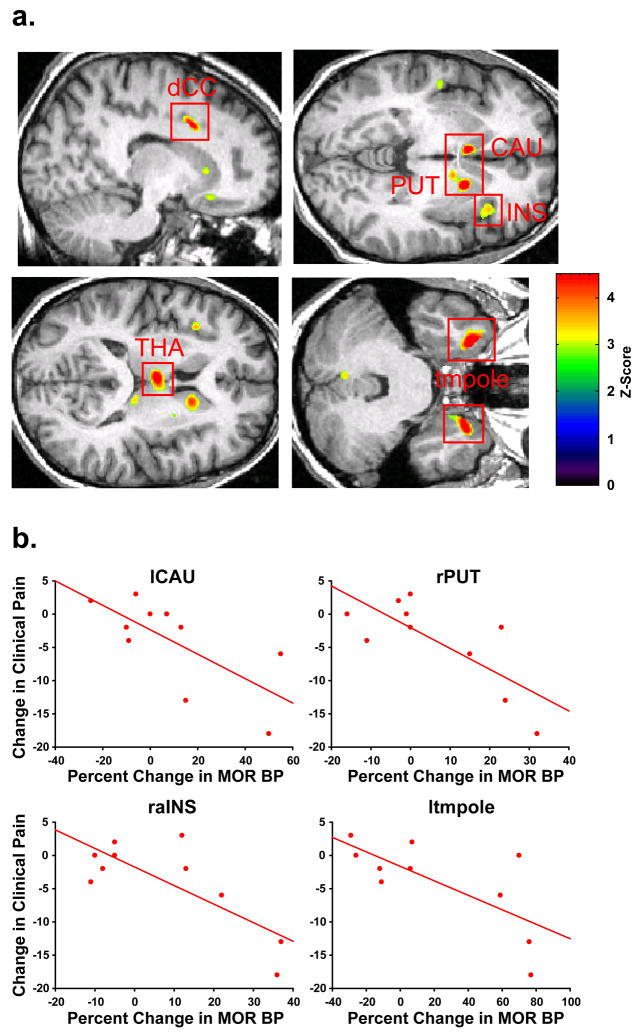
Figure 4.
Long-term Increases in MOR Binding following Acupuncture are Associated with Reductions in Clinical Pain. A) Regions of interest showing negative correlations between changes in MOR BP (baseline2 – baseline1) and changes in clinical pain (pain assessment2 – pain assessment1) following acupuncture. upper left: left dorsal cingulate cortex (ldCC), upper right: left caudate (lCAU), right putamen (rPUT), and right anterior insula (raIns), lower left: left medial thalamus (lmTHA), lower right: bilateral temporal pole (tmpole). B) Scatter plots of percent changes in MOR BP (post-pre) and changes in clinical pain (post-pre) for four regions depicted in A.