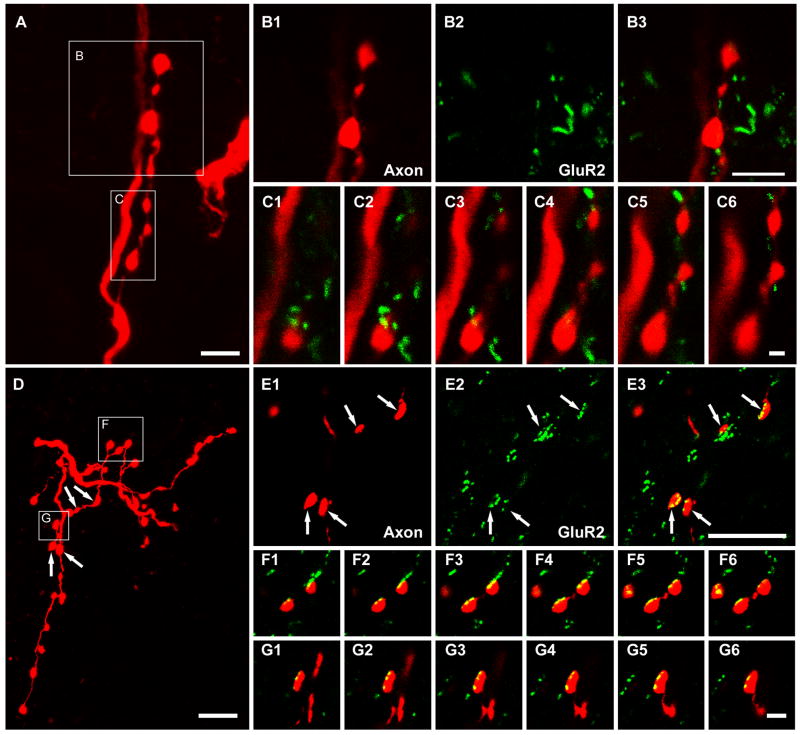
Figure 6.
Relationships between intracellularly labelled axon terminals and immunoreactivity for the GluR2 subunit of the AMPA receptor following antigen unmasking with pepsin. A, B and C show that there is no obvious association between motoneuron axon terminals and GluR2 immunoreactivity. D, E and F show associations between interneuronal axon terminals and immunoreactivity for GluR2. The large panels on the top left (A) and on the bottom left (D) show projected images of a series of terminals originating from a motoneuron and an excitatory interneuron, respectively. Details of the areas demarcated by the boxes are shown in B1-B3, C1-C6, E1-E3, F1-F6, and G1-G6. B1-B3 show motoneuron axon terminals (B1), GluR2 (B2), and a merged image (B3) of the same single optical section. C1-C6 show a series of merged single optical sections through the motoneuron terminals taken at intervals of 0.3 μm. E1-E3 show interneuron axon terminals (E1), GluR2 (E2), and a merged image (E3) of the same single optical section. F1-F6 and G1-G6 show series of merged single optical sections through the interneuron terminals taken at intervals of 0.2μm. Scale bar, 5μm (A, B1-B3, D and E1-E3); 1μm (C1-C6); 2μm (F1-F6, and G1-G6).