Figure 5. Leptin activates JAK/STAT3, MAPK/ERK1/2 and PI-3K/Akt pathways as well as AP1 and NF-κB transcription factors in Kupffer cells.
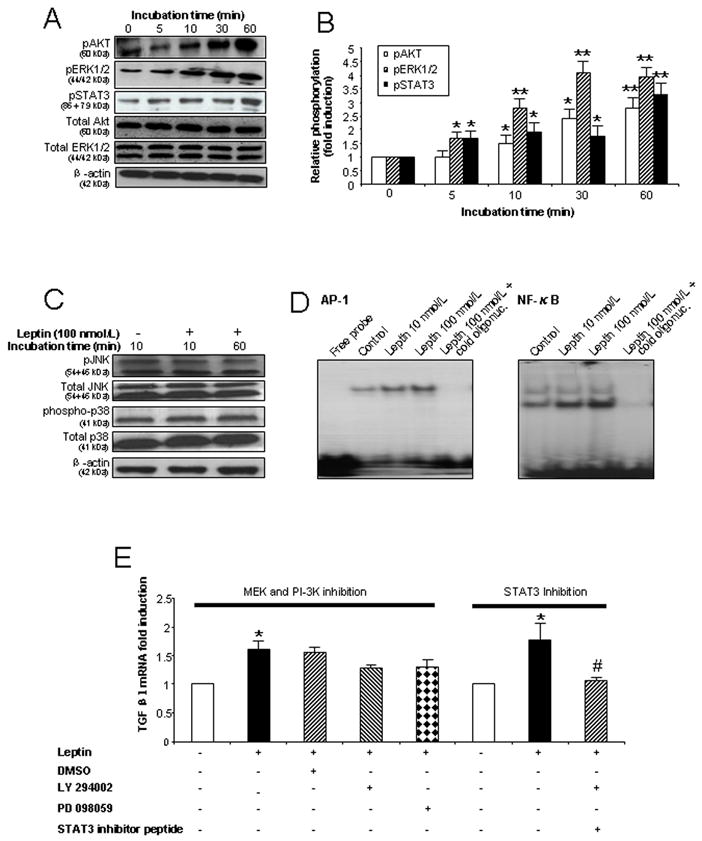
(A) Leptin enhances phosphorylation of STAT3, ERK1/2 and Akt in KCs in a time dependent manner. KCs were exposed to leptin 100 nmol/L for 0, 5, 10, 30 and 60 min and cell lysates used for immunoblot analysis. (B) Densitometry analysis of Fig. 5A as the ratio of p-protein to total protein (ERK1/2 or AKT) or the ratio of pSTAT3 to β-actin. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01 (C) Leptin did not influence phosphorylation of p38 or JNK in KCs. Cell lysates from KCs exposed to leptin 100 nmol/L for 10 or 60 min were used for immunoblotting. (D) Leptin activates AP-1 and NF-κB DNA binding in KCs. Nuclear protein from KCs cultured for 60 min with leptin (10 or 100 nmol/L) was used for EMSA. The disappearance of the shifted band in the presence of a molar excess of unlabeled (cold) oligonucleotide confirms the specificity of the binding. (E). TGFβ1 mRNA expression in KCs in the presence or absence of STAT3 inhibitor peptide (50 μmol/L), a MEK inhibitor (50 μmol/L) and a PI-3K inhibitor (25 μmol/L). RNA was extracted after 24 h treatment. * P < 0.05 and ** P <0.01 vs. control group. # P < 0.05 vs. leptin treatment group without STAT3 inhibitor peptide. Each experiment was conducted in at least 3 independent sets.
