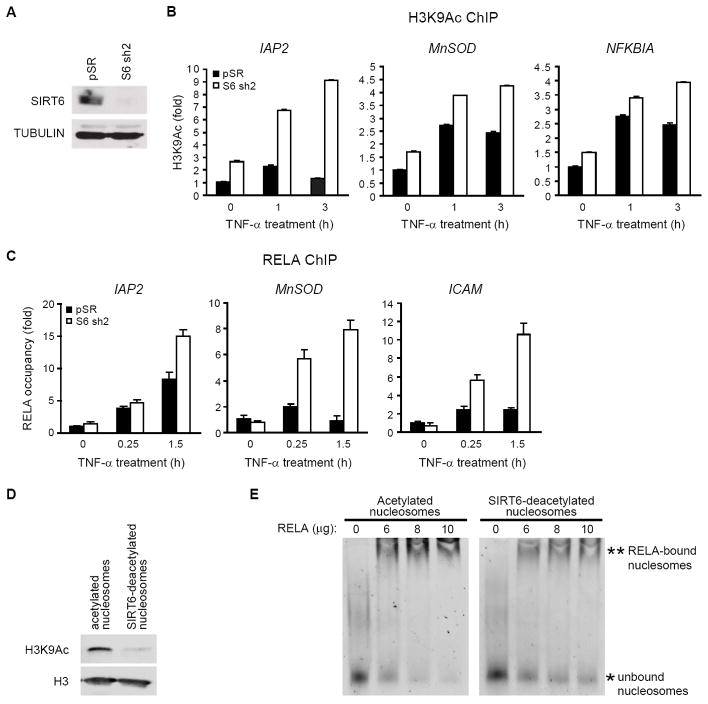
Figure 4. SIRT6 Deacetylates Histone H3K9 at promoters of RELA target genes.
(A) Western analysis of SIRT6 protein in HeLa cells stably expressing SIRT6 shRNA (sh2)
(B) SIRT6 is required for H3K9 deacetylation at promoters of RELA target genes. ChIP with α-H3K9Ac and α-H3 antibodies was performed. H3K9 acetylation at RELA target gene promoters (mean ± s.e.) is shown relative to untreated control samples and normalized to total H3 levels.
(C) SIRT6 is required to limit RELA occupancy at the promoter of RELA target gene promoters. ChIP with α-RELA antibodies was performed following a 30 minute TNF-α pulse; RELA occupancy (mean ± s.e.) at promoters relative to untreated control samples is shown.
(D)-(E) SIRT6-mediated deacetylation of nucleosomes inhibits nucleosome binding to RELA. Western analysis of H3K9Ac levels on nucleosomes following incubation with SIRT6 in NAD-dependent deacetylation or mock reactions (D). The acetylated or SIRT6-deacetylated nucleosomes were used in nucleosome binding assays with increasing amounts of GST-RELA protein (E). Extent of nucleosome binding can be estimated by comparing levels of bound (**) and unbound (*) nucleosomes. Reduced binding is observed in the SIRT6-deacetylated samples (compare 10 ug RELA samples)