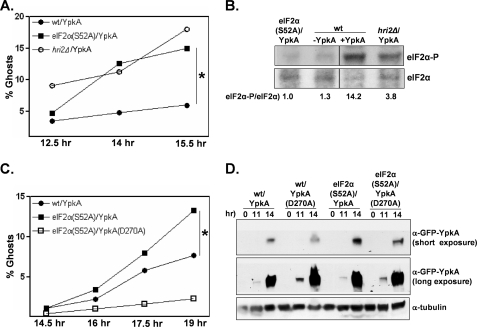
FIGURE 2.
YpkA sensitivity in S. pombe wild-type, eIF2α(S52A), and hri2Δ cells. A, the wild-type (wt), eIF2α(S52A), and hri2Δ strains transformed with plasmids expressing GFP-YpkA driven by a relatively strong promoter (428W, 707W, and 739W, respectively) were subjected to the ghost assay as described in Fig. 1B. B, the indicated strains were propagated and, except where noted, induced for GFP-YpkA expression as described. Cells were collected at 13.5 h, and the resulting whole cell lysates were probed for total and phosphorylated eIF2α by Western analysis. For presentation purposes, the lanes were rearranged. Signals were quantified and normalized to the eIF2α-P/eIF2α ratio observed in the extract derived from the eIF2α(S52A) strain. C, the wild-type (35W) and eIF2α(S52A) (702W and 710W) strains transformed with plasmids expressing either GFP-YpkA or the kinase-inactive GFP-YpkA(D270A) driven by an intermediate-strength promoter were subjected to the ghost assay. D, cells of the transformed strains were collected at the indicated time points, and whole cell lysates were examined by Western analysis. *, p < 0.05 using a two-sample test to compare proportions in two independent samples.