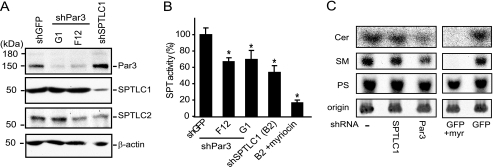
FIGURE 4.
shRNA suppression of Par3 in human THP-1 monocytes inhibits serine palmitoyltransferase activity. A, THP-1 monocytes express Par3, SPTLC1, and SPTLC2 as determined by immunoblotting, and lentivirus-mediated expression of shRNAs targeting Par3 (G1 and F12) or SPTLC1 specifically repress Par3 and SPTLC1 protein expression, respectively. B, lentivirus delivered shRNAs targeting Par3, and SPTLC1 inhibits SPT activity by ∼40% in THP-1 monocytes as determined by measuring the condensation of [14C]serine and palmitoyl-CoA catalyzed by microsomal cell membrane lysates. Pretreatment of the SPTLC1-targeted lysate with the SPT inhibitor myriocin further inhibited activity to 90% (B2 + myriocin, n = 3, ±S.D., *, p < 0.05). C, de novo synthesis of ceramide (Cer) and sphingomyelin (SM) is reduced in cells expressing shRNAs targeting Par3 or SPTLC1 expression as compared with uninfected control cells, or cells expressing a lentivirus-delivered shRNA targeting GFP. As with the Par3- and SPTLC1-targeted cells, myriocin treatment of the control GFP-targeted cells reduced incorporation of [14C]serine into ceramide (Cer) and sphingomyelin (SM) but not phosphatidylserine (PS). Cells were incubated with [14C]serine (5 μCi) for 24 h at 37 °C, and cellular lipids were isolated by chloroform/methanol extraction and separated on TLC plates along with purified standards for ceramide, sphingomyelin, and phosphatidylserine. Labeled lipids remaining at the plate origin was similar demonstrating equal loading of the samples (results representative of two or more independent experiments, and quantification of labeled ceramide and sphingomyelin is shown in supplemental Fig. 5B).