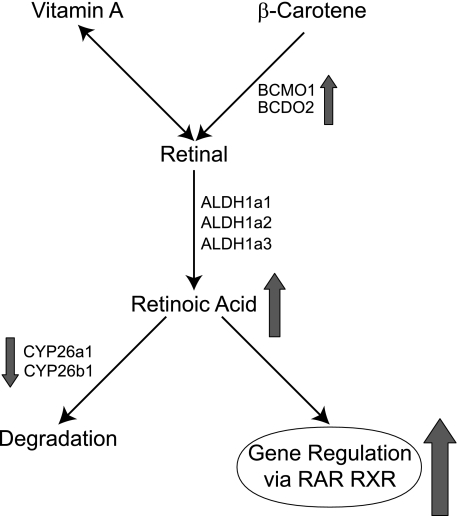
FIGURE 6.
Mechanism for cadmium-induced teratogenicity. Retinoic acid is converted from β-carotene and vitamin A by catabolic enzymes (Bcmo1, Bcdo2, Aldh1a1, Aldh1a2, and Aldh1a3). Excessive retinoic acid can be degraded by P450s (Cyp26a1 and Cyp26b1). Upon cadmium exposure, Bcmo1 levels increase, while Cyp26a1 and Cyp26b1 levels decrease, which causes an increase in the level of RA (arrows). This leads to an increase in retinoid X receptor (RXR) and RAR-mediated transcription.