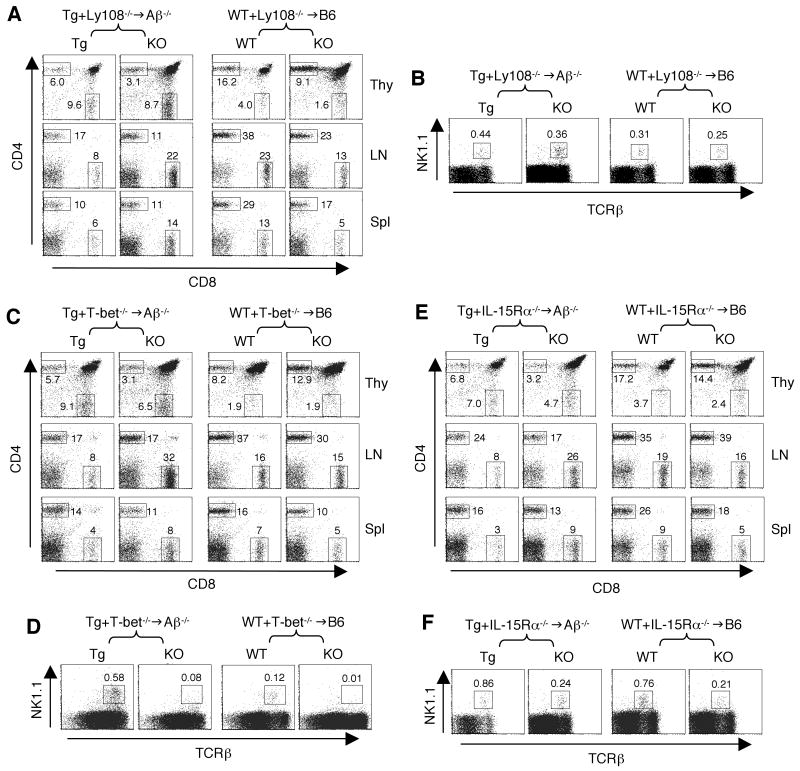
Figure 3. T-CD4 T cell generation in the absence of Ly108, T-bet or IL-15Rα.
(A) CD4 and CD8 profiles of thymocytes, LN and splenic cells from Tg+Lyn-/-→Aβ-/- (left group) and of WT+Ly108-/-→B6 (right group). The numbers in the dot plots show the percentages of gated CD4 and CD8 T cells. The data shown here are one of three chimeras.
(B) A minor defect in Ly108-/- NKT cell generation. The percentage of thymic NK1.1+TCRβ+ NKT cells in Tg+Ly108-/-→Aβ-/- (left two panels) and WT+Ly108-/-→B6 chimeras (right two panels). Numbers indicate the percentages of NKT cells among total thymocytes.
(C) CD4 and CD8 cell populations in thymocytes, LN and splenic cells from Tg+T-bet-/-→Aβ-/- (left panels) and of WT+T-bet-/-→B6 (right panels). The numbers in the dot plots show the percentages of gated CD4 and CD8 T cells. The data shown here are one of three chimeras.
(D) A severe defect in T-bet-/- NKT cell generation in both Tg+T-bet-/-→Aβ-/- and WT+T-bet-/-→B6 chimeric animals. Numbers indicate the percentages of NKT cells among total thymocytes.
(E) CD4 and CD8 profiles from indicated organs in Tg+IL-15Rα-/-→Aβ-/- and WT+IL-15Rα-/-→B6 mice. The numbers in the dot plots show the percentages of gated CD4 and CD8 T cells driven from each BM source. The data shown here are one of three or four chimeras.
(F) IL-15Rα-/- BM had a reduction of the NKT cell population in the mixed BM chimeric mice. Data are representative of 4 individual chimeras. Numbers indicate the percentages of NKT cells among total thymocytes.