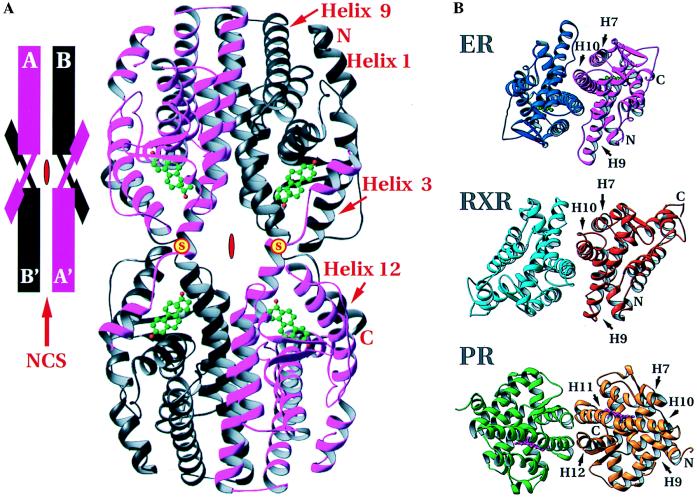
Figure 2.
Arrangement of hERαLBDs in the crystal structure. (A) The tetramer formed by the intermolecular disulfide bonds between Cys-530 of neighboring hERαLBD molecules and dimerization around the local dyad. (Inset) A schematization of the arrangement. Positions of the disulfides are marked with a yellow disc with red “S.” Red symbols in the center of the tetramer and schematic show the crystallographic dyad, and the red arrow in the inset indicates the noncrystallographic symmetry dyad. (B) Comparison of the dimers of holo-hERαLBD, apo-hRXRαLBD, and holo-hPRLBD viewed down the local dyad (17, 18). The dimer interfaces of holo-hERαLBD and apo-hRXRαLBD are similar, with helices 7–10 as the major contributors. The holo-hPRLBD dimer interface is substantially different, composed predominantly of helices 11 and 12, as well as the extreme C-terminal tail. Drawn with ribbons (29).