Figure 1.
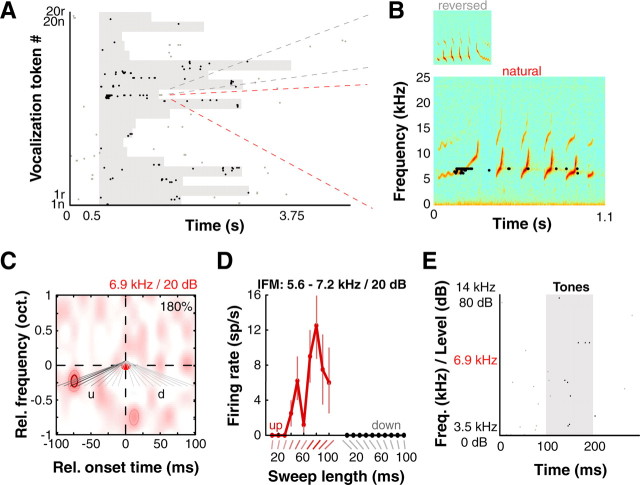
Selectivity for complex features in A1. A, Raster of example neuron's responses to marmoset vocalizations (n, “natural”; r, “reversed”). Gray shading corresponds to stimulus duration; different vocalization tokens had different lengths. Gray and black dots correspond to spontaneous spikes and spikes falling within our analysis window (15 ms after stimulus onset to 50 ms after stimulus offset) respectively. B, Responses to a particular token (“trill-twitter” call and reversed version) showed preference for natural over reversed call. Also note that maximal response occurs immediately following the initial upward-going trill segment. C, This unit responded strongly to a specific combination of two tone pips—a 5.8 kHz pip followed 75 ms later by a 6.9 kHz BF pip (red disk, both pips at 20 dB SPL). Purely second-order interaction map is plotted; image is smoothed for display. Colormap indicates the percentage of facilitation over sum of first-order responses (see Materials and Methods), and dark red contour and pink contour denote significance at p < 0.01 and p < 0.05 (modified permutation test) respectively. The nonlinear component was 180% of the sum of linear components (number in corner of interaction map). Gray lines are diagrams of lFM sweep stimuli tested in D; intensity corresponds to response strength (lightest = 0 spikes/s, darkest = 12.5 spikes/s; u, upward; d, downward lFM sweep direction). D, This unit strongly responded to “up” FM sweeps that connected the RF subunits in the nonlinear map and not to “down” FM sweeps that spanned the same frequency range (mean ± 1 SD plotted). The unit was tuned to an 80-ms-long upward lFM sweep spanning 5.6 kHz to 7.2 kHz (darkest gray line in C), precisely connecting the subunits. E, This unit was unresponsive to pure tones over a wide range of frequencies (2 octaves) and levels around estimated BF and BL (raster shown; frequency and level are interleaved on y-axis).