Figure 7. Conditional deletion of the laminin γ-1 gene from the CA1 region of the hippocampus protects neurons from EW-induced degeneration.
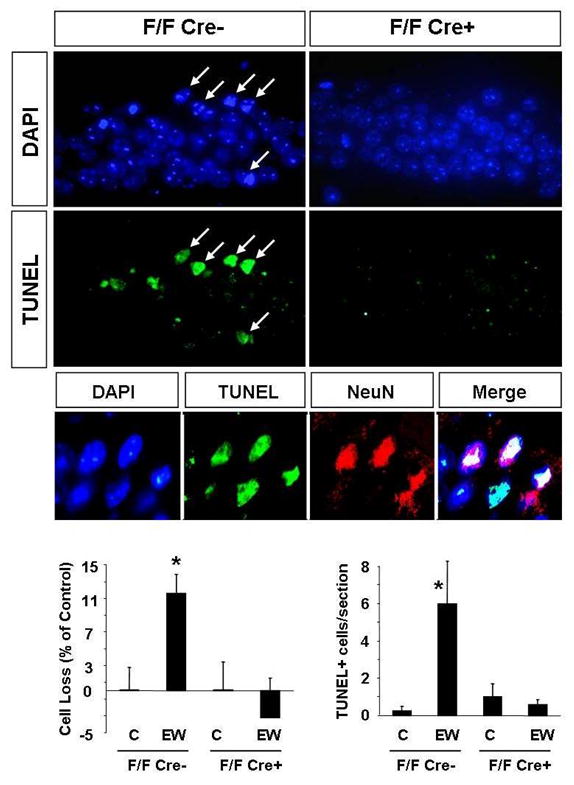
To delete laminin γ-1 in the CA1 region mice in which both copies of the laminin γ-1 gene has been floxed (F/F) were crossed with CaMKIIα-Cre transgenic mice (offspring referred to as F/F Cre+). Immunohistochemistry confirmed a complete absence of laminin γ-1 protein in the CA1 region of F/F Cre+ mice (Chen et al. manuscript in preparation). The F/F Cre- littermates served as controls. The mice were administered EtOH for 14 days and were sacrificed two days following EW. EtOH-naïve mice of the same genotype served as controls. Cell loss was determined by counting cell number in the CA1 region of the hippocampus using DAPI-stained sections. Cell death was further confirmed by visualizing broken DNA strands with the TUNEL method. Analysis of the CA1 region two days after EW revealed that the number of cells decreased in F/F Cre- mice but not in F/F Cre+ animals, in which laminin γ-1 has been deleted (upper panels and quantification in the lower panels). Similarly, we did not observe TUNEL-positive cells in CA1 region of F/F Cre+ mice, typically seen in F/F Cre- (middle panels and quantification in the lower panels) as well as C57/Bl6 animals (see Fig 2 and Fig 3) after EW. Most TUNEL-positive cells colocalized with the neuronal marker NeuN (small middle panels). Sections derived from EtOH-naïve F/F Cre+ and F/F Cre- mice did not show any signs of neurodegeneration and therefore are not shown, but are included in the quantification. * p<0.05; n=4-10 per group for each experiment. The results are presented as mean ± SEM.
