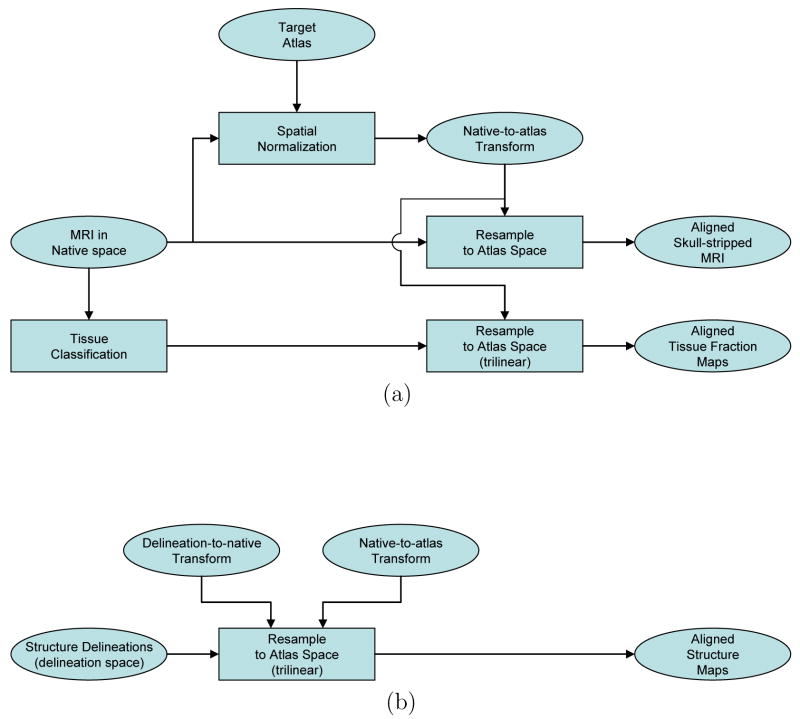
Fig. 4.
These flowcharts show the common approach used in the production of the 3 atlas versions. Once the spatially normalized maps were produced for each subject, they were averaged to produce the average intensity and probability density maps. (a) Normalization of data from native space to the atlas space. The spatial normalization methods and target spaces used are detailed in Table 2. The skull-stripped, RF-corrected MRI were used for the AIR and FLIRT normalization processes; the whole-head MRI were used for the SPM5 normalization. The skull-stripped, RF-corrected MRI were resampled for all 3 versions of the atlas; see the text for details on the resampling parameters used. (b) Normalization of data from delineation space to the atlas space. The delineation labels were separated into individual structure maps and resampled using trilinear interpolation. For the AIR and FLIRT versions of the atlas, this was achieved using a single composited transform; for the SPM5 version, the structure maps were first resampled into the native space, then retransformed into the atlas space. Trilinear interpolation was used in each instance.