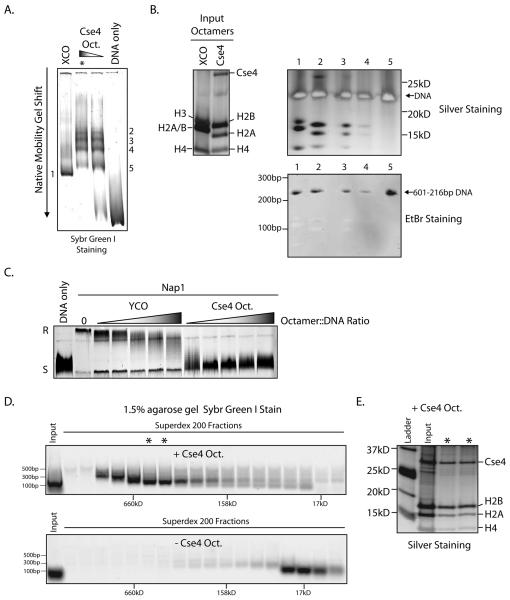
Figure 6.
Reconstitution of Cse4 nucleosomes. A. Cse4 and Xenopus canonical octamers (XCO) were combined with DNA containing the 601-216bp nucleosome positioning sequence and nucleosomes were assembled by salt dilution. The resulting products were resolved on a 5% native poly-acrylamide gel. B. The shifted native gel band from the XCO reconstitution (6A,1) and the bands from the Cse4 reconstitution (6A, 2-5, asterisk) were excised and placed directly into the wells of a denaturing SDS-PAGE gel. This gel was subsequently silver stained and ethidium bromide stained. The top two bands (2-3) from the Cse4 reconstitution contain a full complement of histones and also DNA. C. Both Cse4 and yeast canonical octamers (YCO) were used in a DNA supercoiling assay with recombinant yNap1 as the histone chaperone. Addition of Nap1 and Cse4 octamers to fully relaxed plasmid DNA (R) leads to reversion to a fully supercoiled state (S), an indication of nucleosome deposition onto the plasmid template. D. A supercoiling assay was performed as in 6C, both with and without Cse4 octamers. The reaction was then treated with MNase and loaded onto a Superdex 200 gel filtration column. Fractions were collected and analyzed for DNA content by agarose gel - electrophoresis and Sybr Green I staining. E. Superdex 200 fractions containing ~150bp DNA (6D, asterisks) were treated with Benzonase to digest DNA. These fractions were then analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by silver staining to examine protein content.