Figure 5.
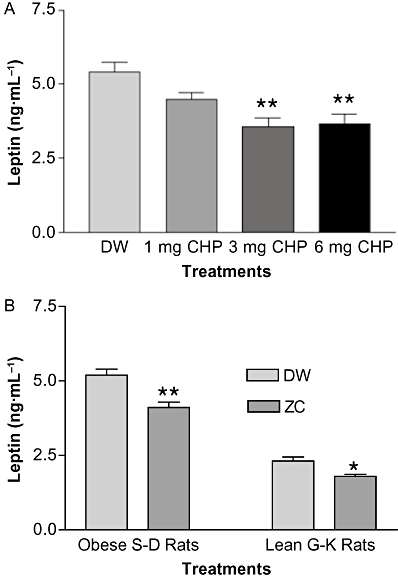
Optimal dose of CHP for the reduction of plasma leptin was determined (A). Overweight or obese aged S-D rats (650–850 g) were divided into four groups of 5–6 rats and treated with drinking water containing either: (i) no additive; (ii) 10-mg zinc plus 1 mg CHP·L−1; (iii) 10-mg zinc plus 3 mg CHP·L−1; and (iv) 10-mg zinc plus 6 mg CHP·L−1 for 15 days. In (B), plasma leptin levels in overweight non-diabetic S-D and lean diabetic G-K rats treated with ZC (zinc + CHP) were determined (B). Fourteen 15-month-old male S-D rats weighing 650–850 g were given drinking water containing no additive or 3-mg CHP plus 10 mg zinc·L−1 and 3-month-old G-K rats were given drinking water containing either no additive or 1-mg CHP plus 10 mg zinc·L−1 for 4 weeks. Rats with the ZC treatments showed reduced leptin level in both aged overweight S-D and lean diabetic G-K rats. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus controls.
