Figure 7.
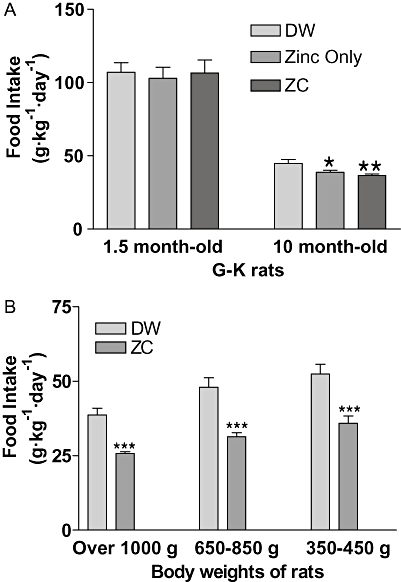
Food intake in relation to initial body weight of animals and ZC treatment in G-K and S-D rats. Thirty 1.5-month-old and thirty 10-month-old G-K rats were divided into three groups of 10 rats respectively, and treated with drinking water containing either no additives, 10 mg·L−1 zinc only or ZC (10-mg zinc plus 1 mg CHP·L−1) for 3 weeks and food intake measured for 3 weeks. No difference in food intake was shown in young rats due to ZC consumption, but in 10-month-old rats, treatment with zinc or with ZC reduced food intake (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01), compared with controls (A). In (B) 6- to 18-month-old S-D rats (n= 18) were divided into three groups of six rats based on their body weights and treated with drinking water containing either no additives or ZC (3-mg CHP + 10 mg zinc·L−1) for 3 weeks. Clear reductions in food intake were observed in all groups of S-D rats receiving ZC water. ***P < 0.001 versus controls (B).
