Figure 4.
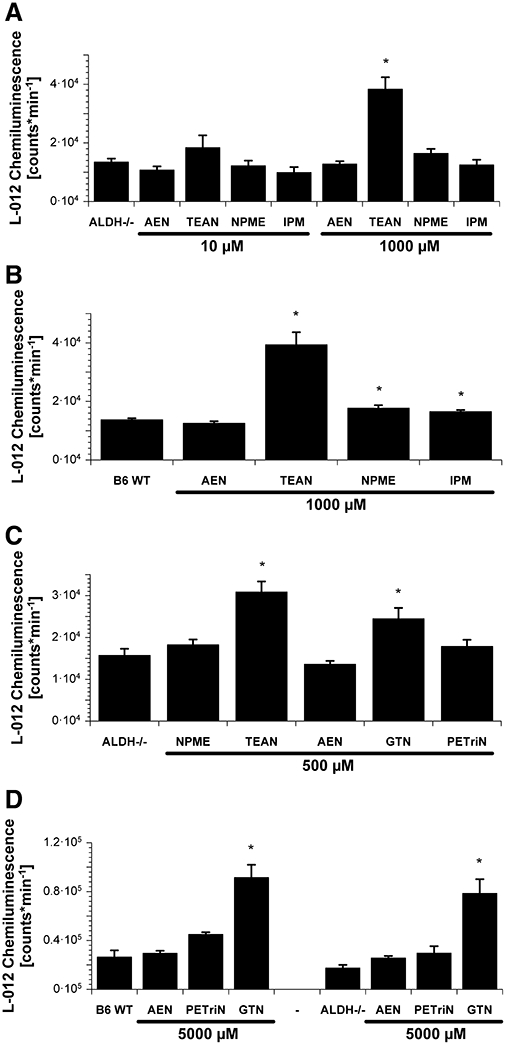
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation after acute organic nitrate treatment. Isolated cardiac mitochondria (0.1 mg protein mL−1) were stimulated with succinate (5 mM), the chemiluminescence signal was detected using a single photon counter in the presence of the dye L-012 (100 µM). The organic nitrates 2-nitrooxyethylammoniumnitrate (AEN), triethanolamine trinitrate (TEAN), methyl-3-nitrooxypropanoat (NPME) and isopropyl nitrate (IPM) were tested at 10 or 1000 µM in mitochondria from ALDH-2−/− (A) or wild-type (WT) (B) mice. ROS formation was also determined for NPME, TEAN, AEN, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) and pentaerithrityl trinitrate (PETriN) at 500 µM in mitochondria from ALDH-2−/− mice (C). Mitochondrial ROS formation in WT versus ALDH-2−/− mice was also measured for AEN, PETriN and GTN at 5 mM (D). All nitrates were used from stocks in dimethyl sulphoxide and the vehicle was added to controls. Data are mean ± SEM of 8–24 (A), 6–24 (B), 8 (C) and 4–6 (D) experiments with mitochondria from three to six animals per group. *P < 0.05 versus untreated control.
