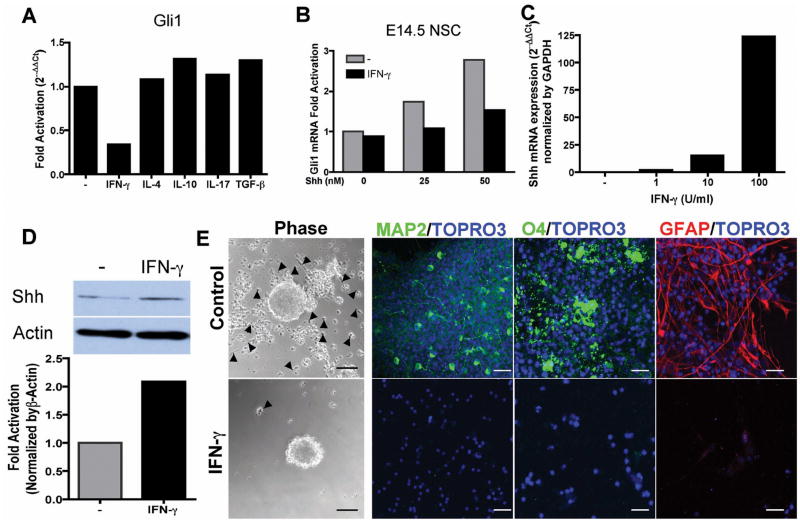
Figure 5. Inflammatory cytokines regulate Shh-Gli1 signaling in NSCs in vitro.
(A) Downregulation of Gli1 expression by IFN-γ. NSCs were treated with Shh together with IFN-γ, TGF-β, IL-4, IL-10 or IL-17 for 48 hours then processed for real-time PCR. (B) Dose response of IFN-γ inhibition of Shh-Gli1 signaling in E14.5 NSCs. (C) Dose response of Shh mRNA expression in E14.5 NSCs treated with IFN-γ for 24 hours by real-time PCR. (D) Western blot analysis of Shh protein expression in E14.5 NSCs-treated with IFN-γ for 48 hours. Densitometry of Shh fold increase normalized to β-actin. (E) IFN-γ abrogates Shh mediated NSC differentiation. E14.5 NSCs were pretreated with Shh for 48 hours and IFN-γ was added for 24 hours followed by FGF/EGF withdrawal for 5 days on PDL-coated coverslips. Phase-contrast images showed that IFN-γ-untreated NSCs attached to PDL surface and migrated out of the neurospheres (arrow head) and immunofluorescent staining revealed NSCs differentiated to neurons (MAP2), oligodendrocytes (O4) and astroglia (GFAP). Whereas, IFN-γ treated cells remained as unattached neurospheres with few cells attached and migrating and no differentiation was observed. Scale bars, 50 μm, phase-contrast, 20 μm immunofluorescence.