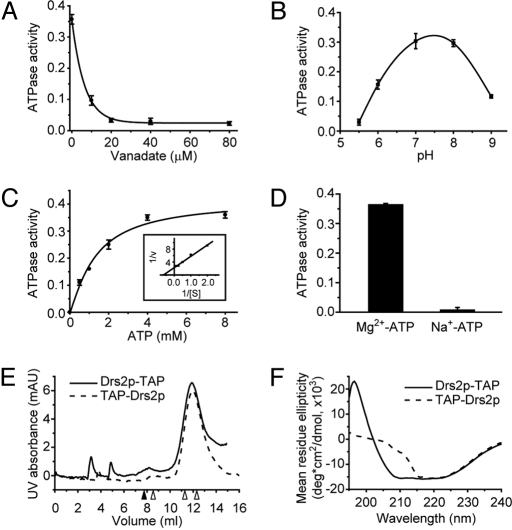
Fig. 3.
Characterization of purified Drs2p in 0.1% C12E9. (A) Sensitivity of TAP-Drs2p ATPase activity to orthovanadate (VO43−). (B) pH profile of TAP-Drs2p ATPase activity assayed as described in Materials and Methods but with varying buffers. pH 5.5 and 6, 50 mM Mes; pH 7, 8, and 9, 50 mM Tris-HCl. (C) Determination of the Km for ATP and Vmax of ATP hydrolysis for TAP-Drs2p. (Inset) Double-reciprocal plot. (D) Mg2+ dependence of TAP-Drs2p ATPase activity. y axis: units of (A) − (D) = μmol Pi released/min/mg Drs2p. (E) Size-exclusion chromatography of purified TAP-Drs2p and Drs2p-TAP using ÄKTA FPLC system and Superose 12 column from GE Healthcare. Samples were injected at 0 mL. The closed arrowhead indicates the void volume (7.77 mL), and the 3 open arrowheads (from left to right) indicate the peaks of ferritin (440 kDa), catalase (232 kDa), and aldolase (158 kDa) standards. (F) Circular dichroism spectra of purified TAP-Drs2p (40 μg/mL) and Drs2p-TAP (38 μg/mL) in 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100 mM NaCl, and 0.1% C12E9.