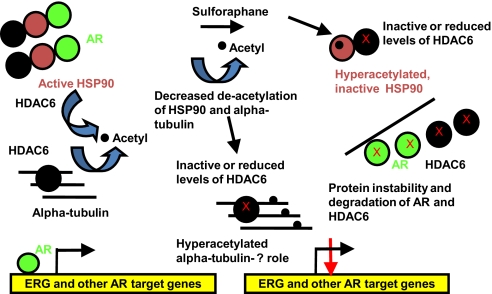
Fig. 7.
Model of sulforaphane attenuation of AR signaling via HDAC6 inactivation. Normally, HSP90 is deacetylated by HDAC6, which enables it to chaperone client proteins such as AR. HDAC6 also deacetylates alpha-tubulin. With sulforaphane treatment, HDAC6 is inhibited or targeted for protein degradation. This leads to hyperacetylated alpha-tubulin; the functional sigificance of this remains unclear. The HDAC6 inactivation with sulforaphane also leads to hyperacetylated, inactive HSP90 protein, which dissociates from AR, and AR is then targeted for protein degradation. Consequently, AR binding to its target gene androgen response elements (ARE), including TMPRSS2-ERG, is diminished, which reduces their expression.