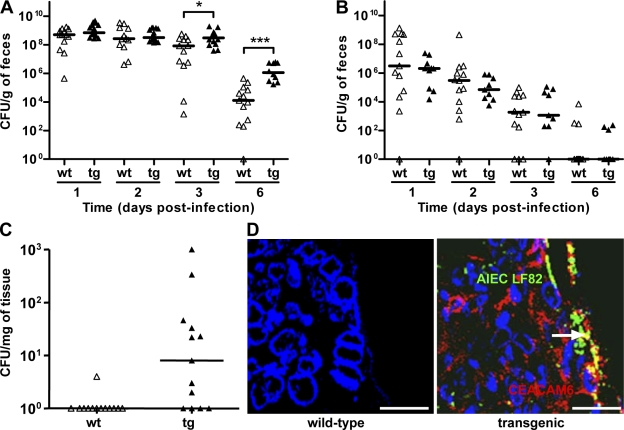
Figure 1.
AIEC LF82 bacterial colonization and persistence in mouse intestine according to CEACAM expression. (A and B) Quantification of AIEC LF82 (A) or E. coli K-12 MG1655 (B) in the feces of WT (wt, white triangles) or CEABAC10 (tg, black triangles) mice receiving 0.25% DSS in drinking water after oral infection with 109 bacteria at day 0. (C) Quantification of colonic mucosal-associated AIEC LF82 bacteria at day 7 after oral infection. The quantification for each mouse (symbols) and the median (bars) is expressed as CFU/g of feces or CFU/mg of organ tissue. (D) Confocal microscopy analysis of colonic section at day 7 after infection from WT or transgenic mice infected with AIEC LF82. CEACAM6 expression was detected using anti-CEACAM6 monoclonal antibody and a Cy3-conjugated anti–mouse IgG. AIEC LF82 bacteria were detected using anti-O83 rabbit antibody and a FITC-conjugated anti–rabbit IgG. Arrow shows colocalization (yellow staining) between CEACAM6 and bacteria. WT FVB/N mice: E. coli K-12 MG1655 infected (n = 13), AIEC LF82 infected (n = 9); CEABAC10 transgenic FVB/N mice: E. coli K-12-MG1655 (n = 13), AIEC LF82-infected (n = 15). Results shown here are representative of three separate colonization experiments. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. Bars, 50 µm.