Figure 1.
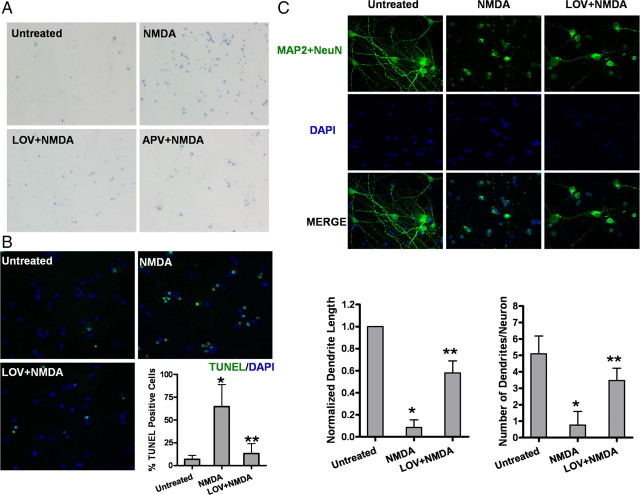
Lovastatin protects NMDA-induced excitotoxicity in primary cultured cortical neurons. A, Representative micrographs of trypan blue-positive cells. Neurons were pretreated with 500 nm LOV for 3 d or 100 μm APV, a specific NMDAR antagonist, for 30 min or left untreated before a 15 min exposure to 100 μm NMDA and 100 μm glycine. Viability was measured by cell counting after trypan blue staining at 24 h after NMDA exposure. B, Representative photographs and quantitative assessment of apoptotic cell death by TUNEL assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.001 versus untreated; **p < 0.001 versus NMDA. C, Photomicrographs showing fluorescence staining of MAP-2 with DAPI. Primary cortical rat neurons were pretreated with 500 nm lovastatin or vehicle for 3 d before exposure to NMDA for 15 min. After fixation, cells were stained with the neuronal markers (MAP-2 and NeuN, green) to delineate the cell morphology, followed by counterstaining with membrane-permeable DAPI (blue). The length of neurites was quantified from 50 of the MAP-2-positive cells, and the number of processes projecting from each positive cell was also quantified. Data are presented in the bar graph as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *p < 0.001 versus untreated; **p < 0.001 versus NMDA.