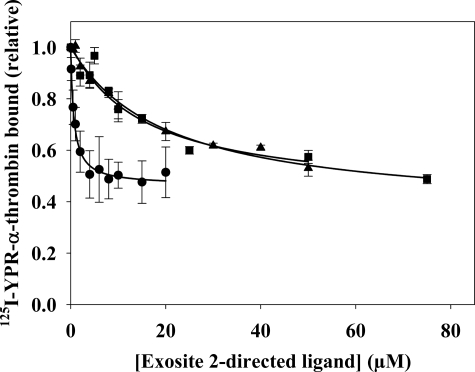
FIGURE 3.
The effect of exosite 2-directed ligands on 125I-YPR-α-thrombin binding to γA/γA-fibrin clots. 20 nm 125I-YPR-α-thrombin and 5 nm α-thrombin were added to microcentrifuge tubes containing 2 μm γA/γA-fibrinogen, 2 mm CaCl2, and HD22 (●), γ′-peptide (▴), or F2 (■) at the indicated concentrations. After incubation for 45 min, clots were pelleted by centrifugation, and free 125I-YPR-α-thrombin in the supernatant was used to calculate the bound fraction. Data are plotted as the relative amount of thrombin bound to the clot versus the concentration of exosite-directed ligand and represent the means ± S.E. of three experiments, each done in duplicate, while the lines represent non-linear regression analysis of the data. HD22 was the most potent of the three ligands, having a Kiobs of 673 ± 83 nm. γ′-Peptide and F2 are less potent than HD22, and reduce thrombin binding with Kiobs values of 15.6 ± 3.8 and 18.5 ± 3.3 μm, respectively.