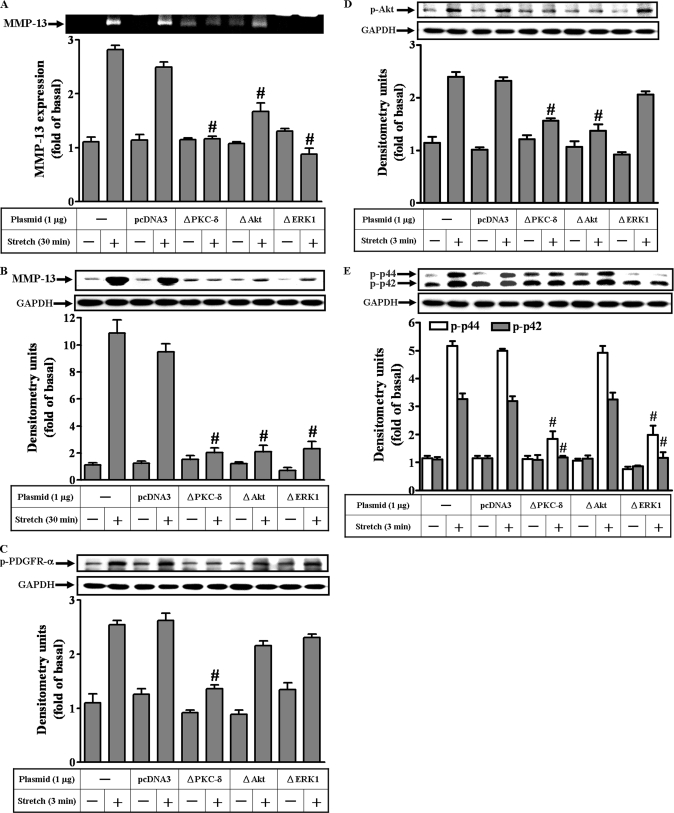
FIGURE 7.
The sequential activation of the signaling molecules in MMP-13 induction by mechanical strain. Dominant negative mutants of the signaling molecules such as ΔPKC-δ, ΔAkt, and ΔERK1 were included to determine the sequential activation. First, the effects of the specific mutants on the strain-induced MMP-13 activities (A) and expressions (B) were examined. The activities and the proteins of the MMP-13 were significantly reduced by the mutants. Next, the effects of the mutants on the phosphorylations of the signaling molecules, including PDGFR-α (C), Akt (D), and p42/p44 MAPK (E) were examined. Among the mutants tested, only ΔPKC-δ inhibited the PDGFR-α phosphorylation (C). The Akt phosphorylations were inhibited by ΔPKC-δ and ΔAkt (D). The phosphorylations of the p42/p44 MAPK were blocked by ΔPKC-δ and ΔERK1. However, ΔAkt did not interfere with p42/p44 MAPK phosphorylation (E). #, p < 0.01, as compared with the control alone. This was a result of three sets of independent experiments.