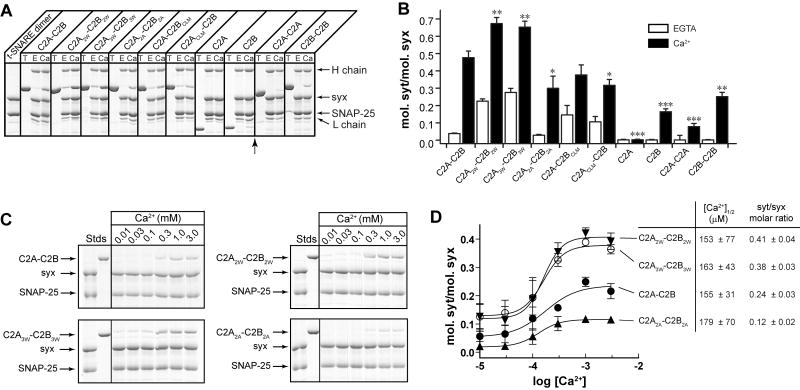
Figure 3. Mutations that alter membrane-bending also affect the ability of syt to bind t-SNAREs.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation (IP) of syt fragments with t-SNARE heterodimers was carried out using an anti-syntaxin (syx) antibody. Equal fractions of total input (T) and immunoprecipitated material (E: 0.2 mM EGTA; Ca: 1 mM Ca2+) were subjected to SDS-PAGE. The 31 samples were resolved in two separate gels, which were juxtaposed at the position indicated by the arrow. (B) t-SNARE binding activity of each syt protein was quantified by densitometry. Data are reported as mean ± SD, n = 3. (C) Trp/Ala mutations within the membrane-penetration loops of syt strongly affect syt's ability to engage t-SNAREs in response to Ca2+, as assessed using co-flotation assays with t-SNARE-bearing, PS-free vesicles. Trp mutants (C2A2W-C2B2W, C2A3W -C2B3W) co-floated more avidly than WT C2A-C2B, while Ala mutant (C2A2A -C2B2A) exhibited diminished binding. (D) Gels in panel C were quantified by densitometry, and molar ratios of syts and syx were plotted against log[Ca2+]. Error bars represent the SEM (n ≥ 3).