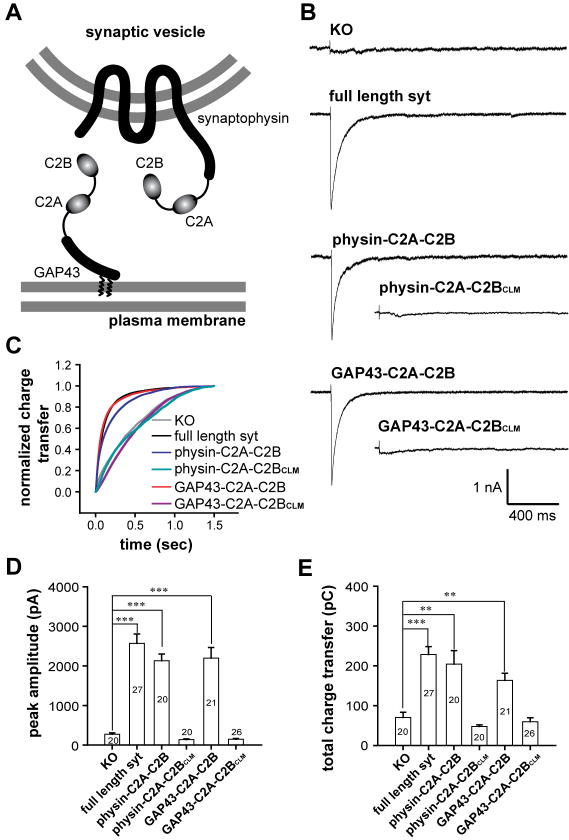
Figure 6. Synaptic vesicle and plasma membrane localized C2A-C2B both rescue rapid exocytosis in syt knock-out neurons.
(A) Diagram showing the C2A-C2B fusion proteins that were expressed in syt I KO neurons. C2A-C2B was targeted to synaptic vesicles by fusing it to the C-terminus of full-length synaptophysin, or was targeted to the presynaptic plasma membrane by fusing it to the first twenty residues of GAP43. (B) Typical traces of evoked IPSCs recorded from syt I KO neurons (KO), and lentivirus infected KO neurons expressing WT syt (syt rescue), GAP43-C2A-C2B, physin-C2A-C2B, GAP43-C2A-C2BCLM or physin-C2A-C2BCLM. (C) Average normalized cumulative IPSC charge transfer over 1.5 s for KO neurons expressing the indicated constructs (D & E) Summaries of the peak amplitude (D) and total charge transfer over 1.5 s (E) of evoked IPSCs.