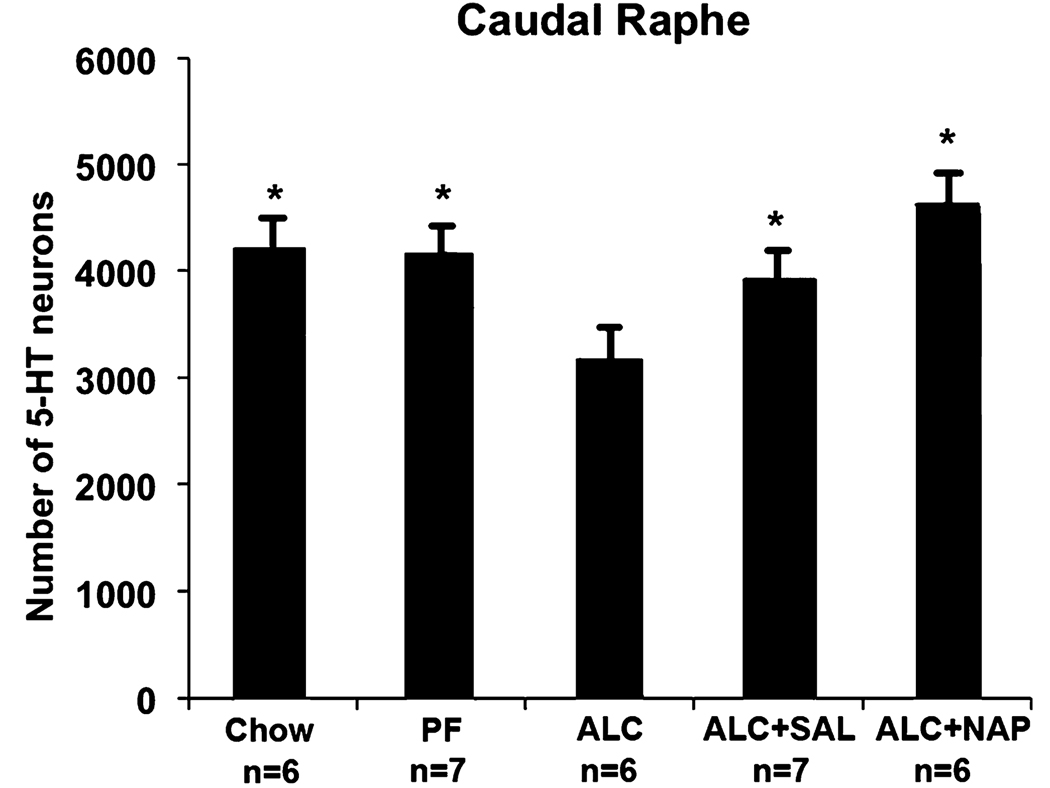
Fig. 5.
Effect of alcohol exposure and NAP and SAL treatment on the number of serotonin (5-HT)-immunostained (5-HT-im) neurons in the caudal raphe. The alcohol treatment significantly reduced the number of 5-HT neurons relative to pair-fed (PF) and Chow controls. Administration of either peptide to the alcohol liquid diet (ALC) group prevented these alcohol-induced deficits, confirmed by the significant increase in the number of 5-HT neurons relative to the vehicle-injected ALC group to a level not different from PF and Chow controls. (*significantly greater than the ALC group, but not different from each other). ALC, alcohol liquid diet; SAL, activity-dependent neurotrophic factor agonist peptide (SALLRSIPA); NAP, activity-dependent neurotrophic protein agonist peptide (NAPVSIPQ).