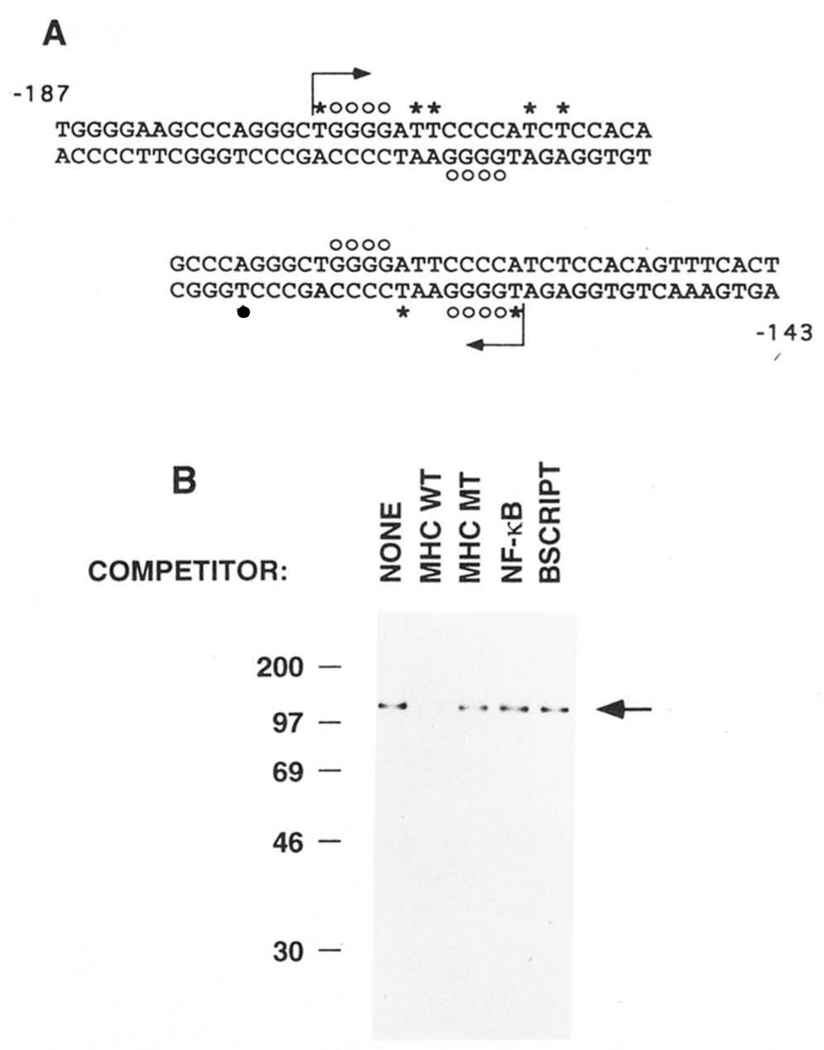
FIG. 3. UV cross-linking of purified H2TF1 to the MHC class I site.
H2TF1, purified by three affinity steps (SDS-PAGE shown in Fig. 2B), was cross-linked by UV irradiation to MHC κB site probes substituted with BrdUrd and 5′ 32P-dC as indicated below. Competitor DNA species, where indicated, were present in 60-fold excess. The binding reactions were incubated and cross-linked as described under “Materials and Methods.” A, DNA sequences of the MHC κB site probes used in the UV cross-linking experiments. The sequences span from −187 to −143 bp upstream from the MHC H2-Kb transcription start site and include the MHC κB site centered at −166 bp. The probe beginning at −187 bp was designated “−187” and the probe ending at −143 bp was designated “−143.” The −187 probe was made by hybridizing a 16-base oligonucleotide primer to the 37-base oligonucleotide bottom strand and then filling in the single stranded gap by synthesis with DNA polymerase I Klenow fragment, as indicated by the starting position and direction of the arrow, allowing substitution of the probe with BrdUrd and 32P-dC. The −143 probe was similarly made. The asterisks mark the dT nucleotides replaced with BrdUrd. The dC nucleotides added in the direction of the arrow were labeled with 32P on their 5′ side. The open circles mark the dG nucleotides which, when methylated, interfere with the binding of H2TF1 (Baldwin and Sharp, 1988). B, SDS-PAGE of the complexes obtained by UV cross-linking purified H2TF1 (Fig. 2B) to the −143 probe. The cross-linking reactions were done in the absence and presence of the indicated competitor DNA species (see “Materials and Methods” for sequences). The arrow indicates the position of a protein of 110,000 Mr, specifically cross-linking to the −143 probe, competed by wild type (MHC WT) competitor, but not by double point mutant (MHC MT), NF-κB site (NF-κB), or Bluescript poly-linker (BSCRIPT) competitors. A similar result was obtained with the −187 probe and H2TF1 purified by two affinity steps (data not shown). The molecular weight standards, labeled with 14C methylation (Amersham C626), were myosin (200,000), phosphorylase b (97,400), BSA (69,000), ovalbumin (46,000), and carbonic anhydrase (30,000).