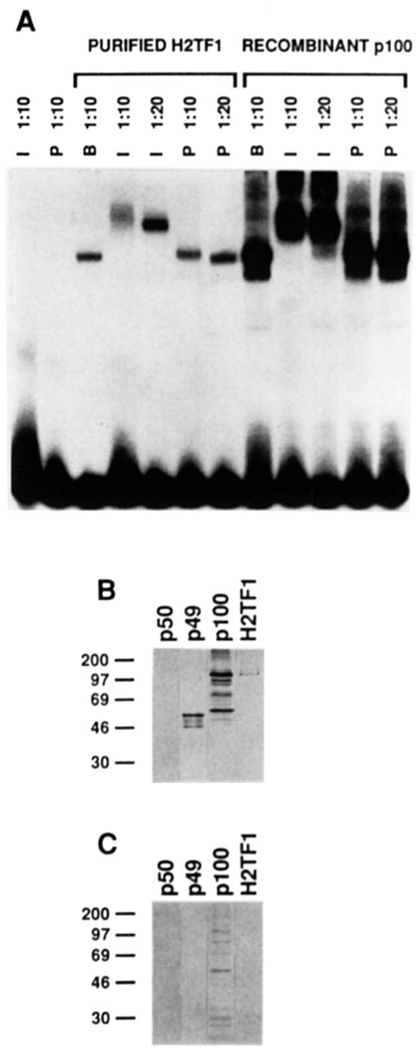
FIG. 7. H2TF1 is recognized by antiserum raised against an 18-amino acid peptide from the NH2 terminus of NF-κB2 p100.
A, supershift of H2TF1 and recombinant NF-κB2 pl00 complexes by an antiserum specific for the NH2-terminal peptide of the NF-κB2 pl00 protein. The gel shift. reactions were assembled and electrophoresed as described under “Materials and Methods.” The H2TF1 tested (Purified H2TF1) was purified by three affinity steps (SDS-PAGE shown in Fig. 2B). The recombinant NF-κB2 pl00 tested (Recombinant p100) was overproduced in 293 cells (immunoblot shown in B and C, lane p100). Both immune (I) and preimmune (P) sera were tested at either 1:10 or 1:20 dilution, as indicated, and antiserum dilution buffer (B) was tested at a 1:l0 dilution. Control reactions with antisera alone are also shown. B, immunoblot of H2TF1 and recombinant Rel family proteins developed with the immune antiserum used in A. The immunoblot procedure was performed as described under “Materials and Methods.” Equivalent amounts (10 ng, estimated by DNA-binding activity) of human NF-κB1 p50, NF-κB2 p49, and NF-κB2 pl00 were tested in lanes p50, p49, and p100, respectively. An equivalent amount of H2TF1 (10 ng, estimated by DNA-binding activity), purified by two affinity steps, was tested in lane H2TF1. C, immunoblot as in B, but the immune antiserum was blocked with the NF-κB2 pl00 NH2-terminal peptide to which it was raised (at 2 mg/ml; sequence presented under “Materials and Methods”) prior to development of the blot.