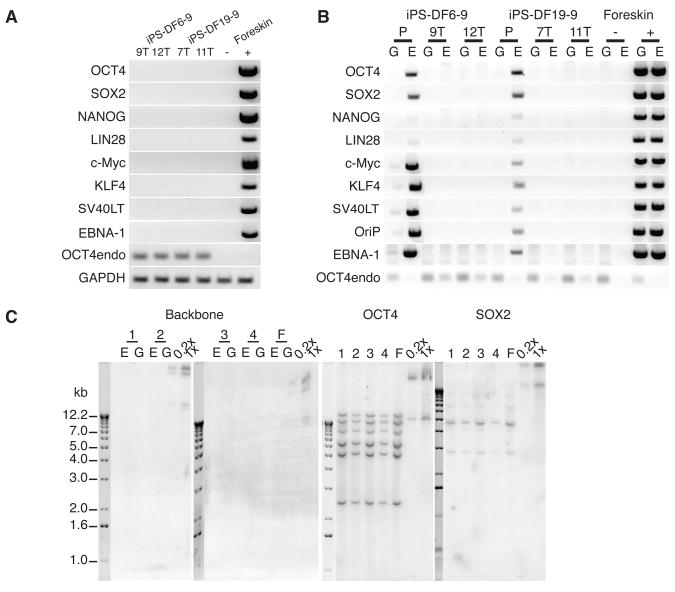
Fig. 2.
Human foreskin fibroblast-derived iPS cells free of vectors and transgenes. (A) RT-PCR analysis of transgene expression in iPS-DF6-9 subclone 9T and 12T, and iPS-DF-19-9 subclone 7T and 11T. Negative control (−): fibroblasts. Positive control (+): fibroblasts transfected with combination 19 episomal vectors (day 4 posttransfection). 32 PCR cycles were used for all primer sets. (B) PCR analysis of episomal DNA in iPS-DF6-9 (P: parental clone), iPS-DF6-9 subclone 9T and 12T, iPS-DF19-9 (P), and iPS-DF19-9 subclones 7T and 11T. G: genomic DNA template; E: episomal DNA template. Negative (−) and positive (+) controls were the same as in Fig. 1E. 32 PCR cycles were used for all primer sets except OCT4endo (28 cycles). (C) Southern blot analysis of exogenous DNA in iPS-DF6-9 and iPS-DF-19-9 subclones. The pCEP4 vector was used as a probe to detect the presence of vector backbone, and the open reading frames of OCT4 and SOX2 were used as probes to examine both the endogenous gene and possible transgenes. 1: iPS-DF6-9-9T; 2: iPS-DF6-9-12T; 3: iPS-DF19-9-7T; 4: iPS-DF19-9-11T; F: foreskin fibroblasts. E: undigested episomal DNA; G: digested genomic DNA. Combination 19 episomal vector DNA diluted to the equivalents of 0.2 and 1 integration per genome was used as positive controls (0.2x and 1x).