Fig 4.
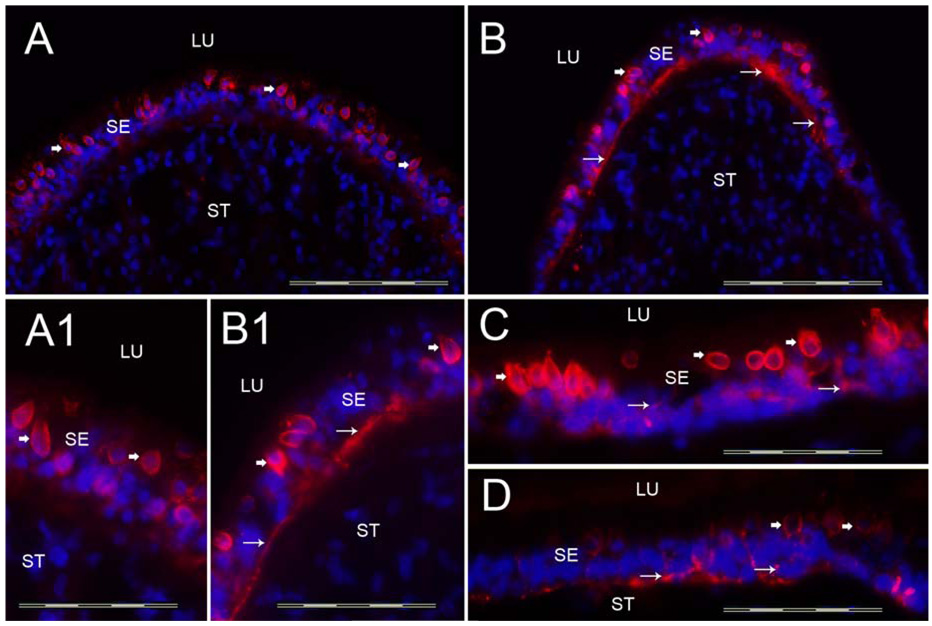
Tenascin-C-IR. Fig 4A shows a cross-section of the crista ampullaris at the planum semilunatum. Fig 4B shows tenascin-C-IR at the central region of the crista ampullaris. Tenascin-C-IR (red color) was found in calyx-like profiles (arrowheads) throughout the SE and also in BM underneath the SE (arrows). Tenascin-C-IR was more prominent in the central portion of the crista (Fig 4B) than in the BMs underneath the SE in the planum semilunatum of the crista (Fig 4A). Figure 4A1 and 4B1 is a high magnification view (from Fig 4A and 4B) of these areas to demonstrate the tenascin-C-IR pattern. The macula utricle (Fig 4C) and the macula saccule (Fig 4D) exhibited similarly tenascin-C-IR in calyx-like structures (arrowheads) and within the BMs underneath the SE (arrows). DAPI (blue color) identifies cell nuclei. Magnification bar is 200µm for Fig A, B, C and D; 50 µm for fig A1, B1.