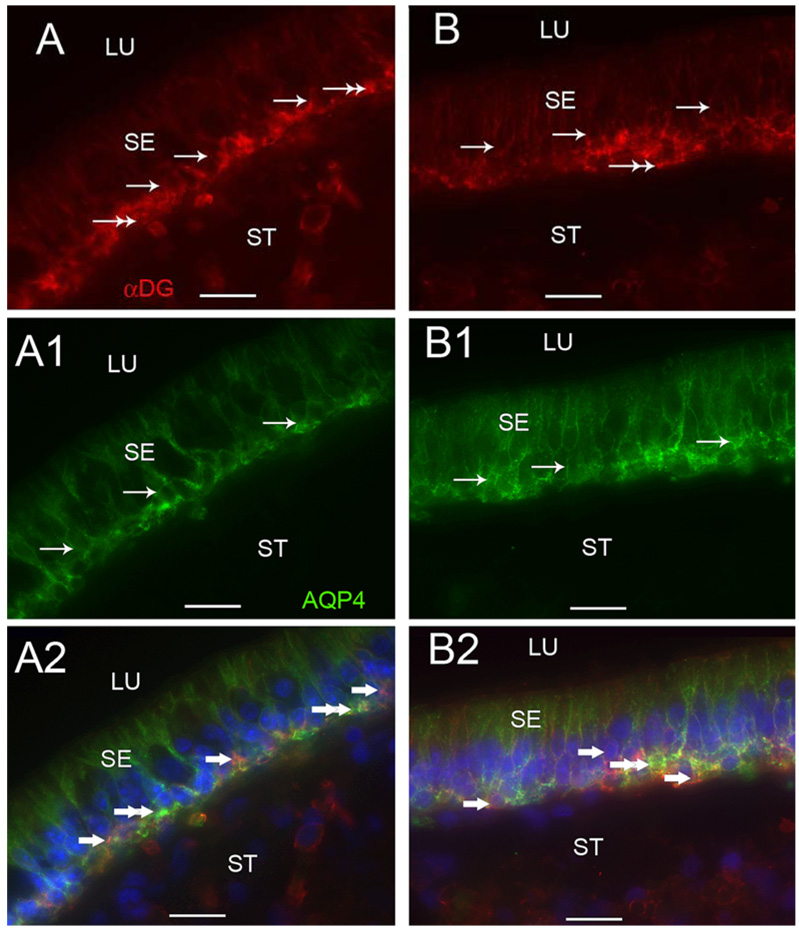
Fig 7.
α-Dystroglycan-IR and AQP4-IR co-distribution in vestibular supporting cells. Fig 7A, 7A1 and 7A2 are cross-sections of the crista ampullaris, near the central region. Fig 7A demonstrates α-dystroglycan-IR (red color) localized to the basal pole of supporting cells (arrows) and to the BM underlying the sensory epithelium (SE) (double arrows). Fig 7A1 demonstrates AQP4 (green color) localization to the basolateral portion of the supporting cells (arrows); the BM underlying the SE and the perineural and perivascular BMs in the stroma (ST) did not exhibit AQP4-IR. Fig 7A2 is a merged image from 7A and 7A1 to illustrate the co-distribution and co-localization of α-dystroglycan and AQP4. α-dystroglycan in red color (arrowheads) segregated to the stromal (ST) perineural BMs and appeared to segregate to portions of the BM underlying the sensory epithelium (SE). AQP4 (green color) appeared to co-localize with α-dystroglycan (red color) with resulting yellow color within the basal supporting cells (double arrowheads). Fig 7B, 7B1 and 7B2 are cross-sections of the macula utricle. Fig 7B demonstrates that αdystroglycan-IR (red color) localized to the basal supporting cells (arrows) and the BM underlying the SE (double arrows). Fig 7B1 demonstrates that AQP4-IR (green color) localized to basolateral supporting cells (arrows). Fig 7B2 is a merged micrograph demonstrating the co-localization of α-dystroglycan and AQP4 (yellow color at double arrows) in the basolateral aspect of the utricular supporting cells. Magnification bar is 25 µm for all figures.