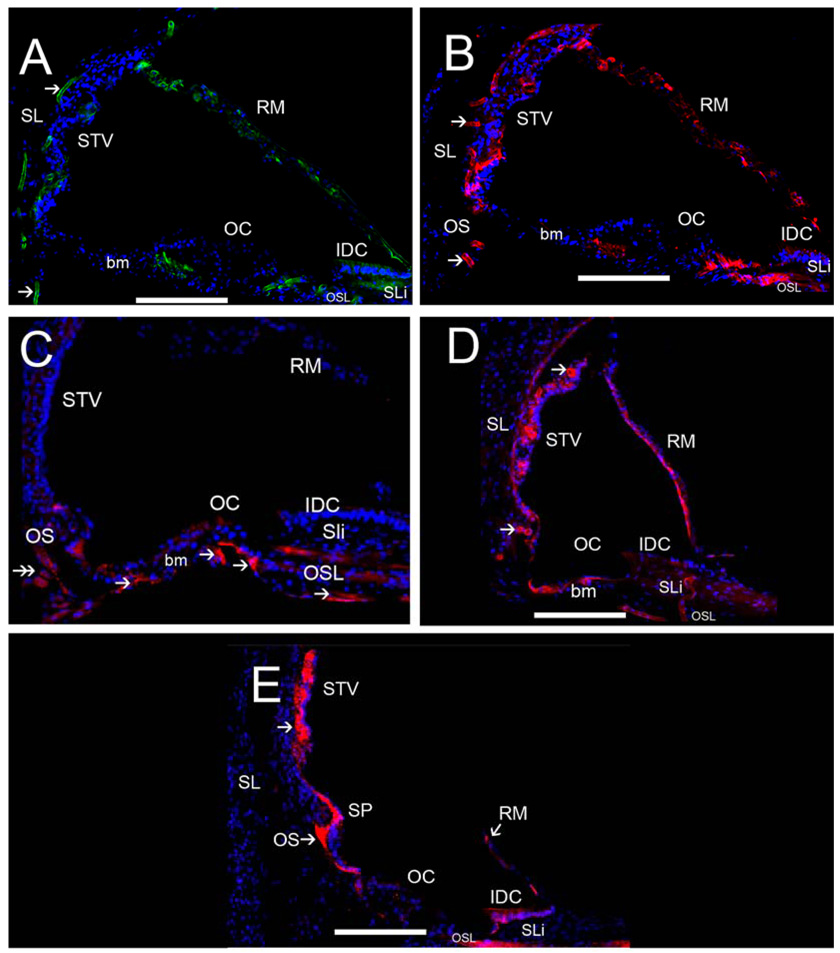
Fig 8.
ECM protein-IR in the human cochlea. Fig 8A exhibits strong collagen IVα2-IR in strial and spiral ligamental perivascular BMs (arrowheads), less intense collagen IVα2-IR was seen at the interdental cells (IDC) and basilar membrane (bm). Collagen IVα2 was expressed in Reissner’s membrane (RM). Fig 8B shows strong nidogen-IR in strial and spiral ligamental perivascular BMs (arrowheads), in the IDC, in RM and the osseous spiral lamina (OSL). Fig 8C demonstrates tenascin-C-IR within BMs of the basilar membrane underneath the supporting cells in the pars arcuata (PA) and pars pectinata (PP) and within the OSL (double arrowhead). Tenascin-C-IR was also seen in the basal portion of the Rosenthal canal (RC). Fig 8D shows laminin-β2-IR within most cochlear BMs including the strial and spiral ligamental perivascular BMs (arrows), in RM, and the IDC, and in the basilar membrane. Fig 8E demonstrates α-dystroglycan-IR within most cochlear BMs (arrowheads) with strong IR in cells of the outer sulcus (OS), the IDC, RM, the spiral prominence and stria vascularis perineural BMs. The inner and outer hair cells and the supporting cells in the organ of Corti (OC) were not reactive for any ECM proteins. All of the basement membrane proteins were expressed to differential degrees within Reissner’s membrane, the basilar membrane, and the interdental cells. Perineural and perivascular BMs in the STV and the spiral ligament (SL) expressed collagen α2IV, nidogen and laminin-β2. The tectorial membrane was not visualized because it had become detached during the microdissection of the cochlea. Magnification bar is 100 µm for all figures.