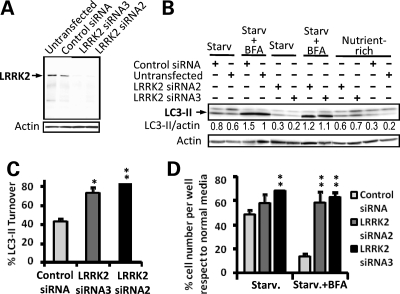
Figure 6.
LRRK2 knockdown increases autophagic activity and prevents Bafilomycin-induced cell death under starvation. (A) Demonstration of siRNA mediated LRRK2 knockdown. siRNA mediated knockdown of wild-type Ypet-LRRK2 in clonal cell lines carrying BAC-YPet-LRRK2-WT-FRT shown by western blot using anti-GFP antibodies. Forty micrograms of protein were loaded per lane. (B) Upon LRRK2 knockdown, LC3-I and LC3-II endogenous expression was assessed by western blot under nutrient-rich or 4.5 h starvation in HBSS with or without 200 nM of the autophagic inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (BFA). Ten micrograms of protein were loaded per lane. Mean LC3-II densitometric relative values versus actin of three experiments are shown. (C) Quantification of LC3-II turnover under starvation upon LRRK2 siRNA knockdown after normalization against actin using a densitometric analysis. The amount of LC3-II under starvation was subtracted from the amount of LC3-II under starvation in the presence of the inhibitor of late stages of autophagy BFA, and the difference expressed as a percentage relative to the amount of LC3-II under starvation in the presence of BFA. (D) Quantification of the relative amount of cells per well surviving 4.5 h of starvation treatment in HBSS with or without BFA upon LRRK2 knockdown with respect to nutrient rich conditions. Values are expressed as percentages against the values obtained from cells cultured in normal media for each condition. Bars represent mean + SEM. Experiments were performed in triplicate. Statistical comparisons are made against the control using Student's t test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.