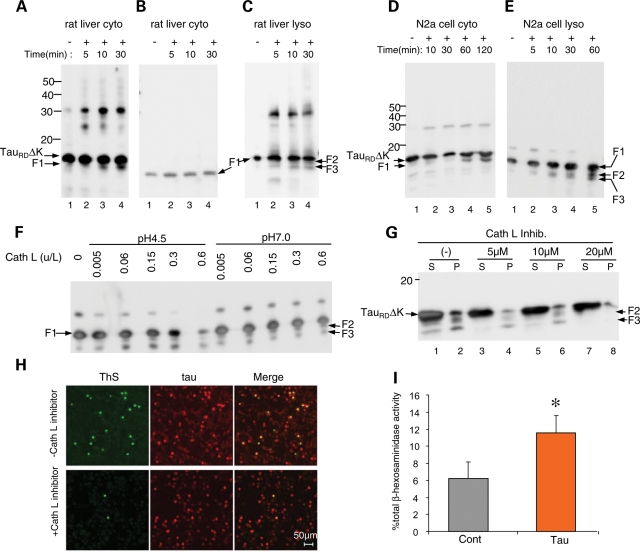
Figure 3.
Cleavage of Tau constructs by cytosol, lysosomal matrix or cathepsin L and release of lysosomal hydrolase β-hexosaminidase into the cytosol of N2a cells caused by expression of TauRDΔK. (A) TauRDΔK incubated with cytosol fraction from rat liver. Note the appearance of fragment F1 (but not F2 or F3) and oligomeric aggregates (mostly dimers). (B) F1 incubated with cytosol fraction from rat liver. Note that there is no cleavage of F1. (C) F1 incubated with lysosomal matrix fraction from rat liver. Note cleavage of F1 to F2 and F3, as well as generation of oligomers (dimers and trimers). (D) TauRDΔK incubated with cytosol fraction from N2a cells. Note appearance of fragment F1 and oligomers. (E) F1 incubated with lysosomal fraction from N2a cells. Note fragmentation to F2 and F3. (F) Digestion of F1 by cathepsin L. Recombinant F1 (0.1 µg/µl) was incubated with 0.005, 0.06, 0.15, 0.3 or 0.6 U/l cathepsin L in 100 mm Na acetate pH 4.5 or 100 mm Tris–HCl pH 7.0 for 60 min. Note that fragments F2 and F3 (arrows) are generated by cathepsin L at both pH 7.0 and pH 4.5. (G) Cathepsin L inhibitor reduces generation of F2 and F3. N2a cells expressing TauRDΔK were treated with cathepsin L inhibitor for 3 days at concentrations up to 20 µm. Lanes labeled P (=pellet) denote sarkosyl-insoluble Tau species, S (=supernatant) indicates soluble proteins. (H) Cathepsin L inhibition also inhibits aggregation of Tau. N2a cells expressing TauRDΔK were treated without or with cathepsin L inhibitor for 3 days. ThS staining reveals that inhibition of cathepsin L reduces Tau aggregation as well. (I) Expression of TauRDΔK causes the release of lysosomal hydrolase β-hexosaminidase. N2a cells expressing TauRDΔK were induced to express Tau for 2 days. The cytosolic distribution of β-hexosaminidase is expressed as the percentage of total β-hexosaminidase activity and is shown as mean ± SEM of four different experiments (*P < 0.05).