Abstract
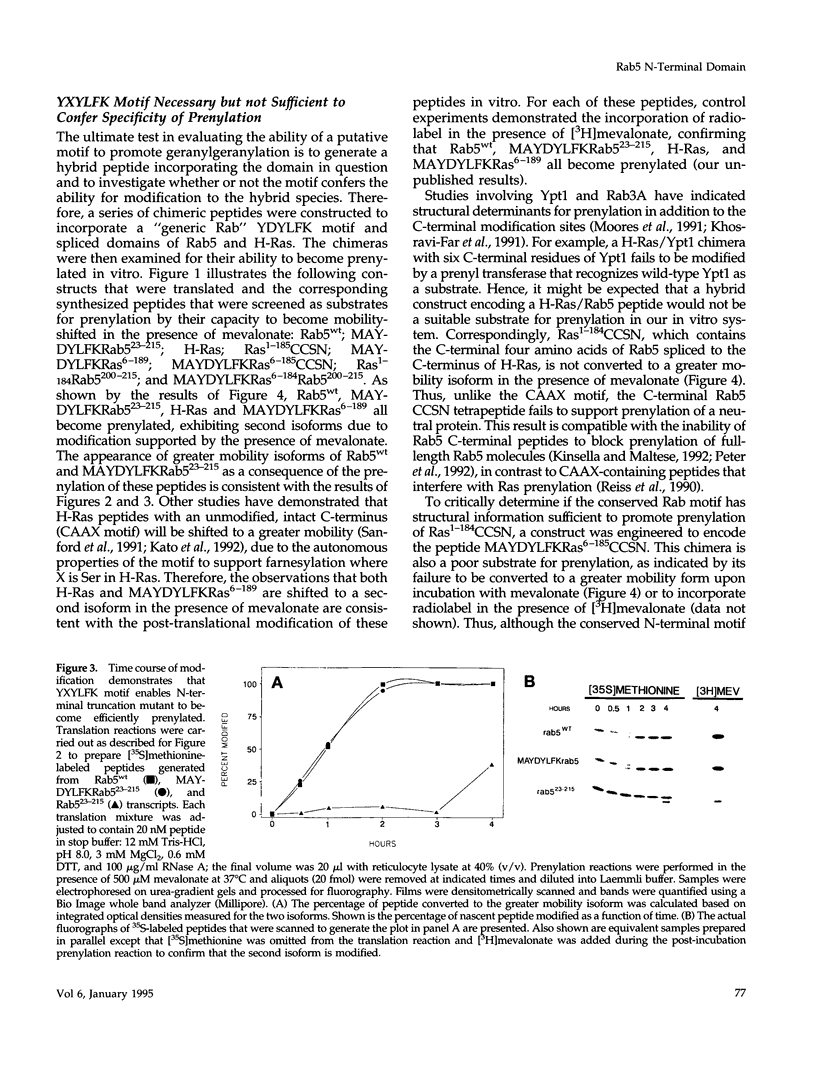
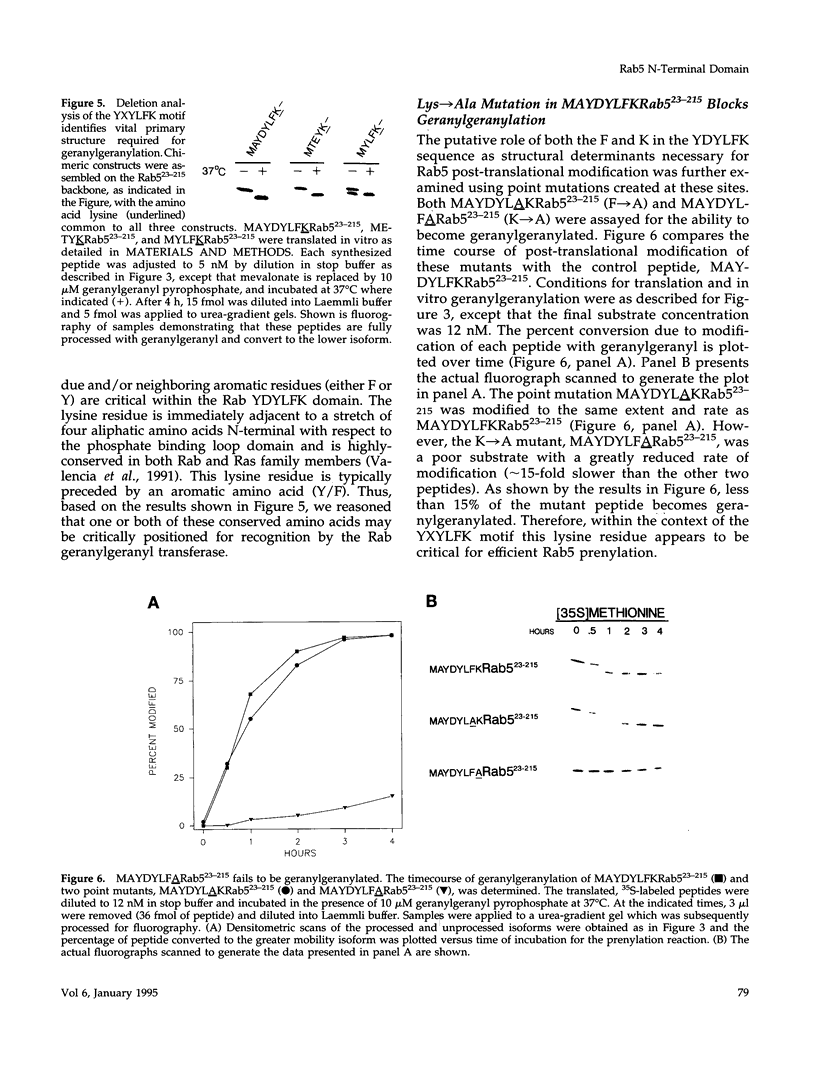
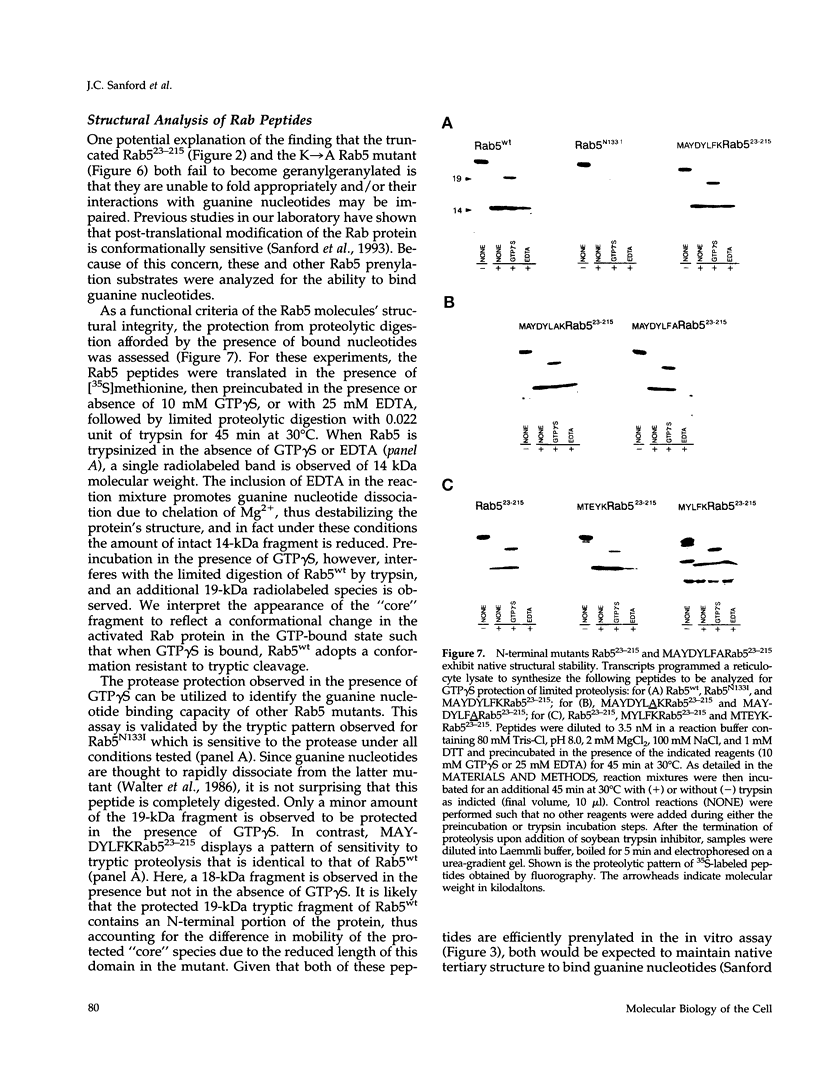
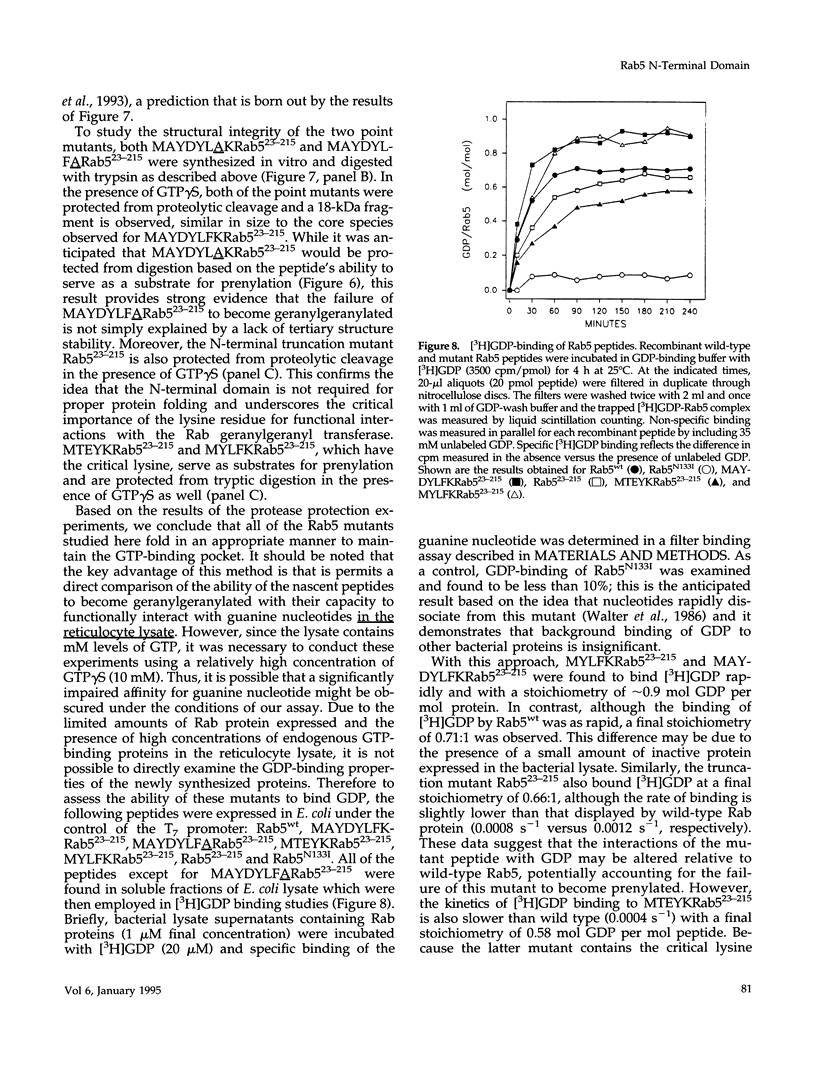
Rab5 is a Ras-related GTP-binding protein that is post-translationally modified by prenylation. We report here that an N-terminal domain contained within the first 22 amino acids of Rab5 is critical for efficient geranylgeranylation of the protein's C-terminal cysteines. This domain is immediately upstream from the "phosphate binding loop" common to all GTP-binding proteins and contains a highly conserved sequence recognized among members of the Rab family, referred to here as the YXYLFK motif. A truncation mutant that lacks this domain (Rab5(23-215) fails to become prenylated. However, a chimeric peptide with the conserved motif replacing cognate Rab5 sequence (MAYDYLFKRab5(23-215) does become post-translationally modified, demonstrating that the presence of this simple six amino acid N-terminal element enables prenylation at Rab5's C-terminus. H-Ras/Rab5 chimeras that include the conserved YXYLFK motif at the N-terminus do not become prenylated, indicating that, while this element may be necessary for prenylation of Rab proteins, it alone is not sufficient to confer properties to a heterologous protein to enable substrate recognition by the Rab geranylgeranyl transferase. Deletion analysis and studies of point mutants further reveal that the lysine residue of the YXYLFK motif is an absolute requirement to enable geranylgeranylation of Rab proteins. Functional studies support the idea that this domain is not required for guanine nucleotide binding since prenylation-defective mutants still bind GDP and are protected from protease digestion in the presence of GTP gamma S. We conclude that the mechanism of Rab geranylgeranylation involves key elements of the protein's tertiary structure including a conserved N-terminal amino acid motif (YXYLFK) that incorporates a critical lysine residue.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderegg R. J., Betz R., Carr S. A., Crabb J. W., Duntze W. Structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating hormone a-factor. Identification of S-farnesyl cysteine as a structural component. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18236–18240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres D. A., Seabra M. C., Brown M. S., Armstrong S. A., Smeland T. E., Cremers F. P., Goldstein J. L. cDNA cloning of component A of Rab geranylgeranyl transferase and demonstration of its role as a Rab escort protein. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1091–1099. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E. Biochemistry of interorganelle transport. A new frontier in enzymology emerges from versatile in vitro model systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):16965–16968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucci C., Parton R. G., Mather I. H., Stunnenberg H., Simons K., Hoflack B., Zerial M. The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):715–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90306-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Gorvel J. P., Stelzer E., Simons K., Gruenberg J., Zerial M. Hypervariable C-terminal domain of rab proteins acts as a targeting signal. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):769–772. doi: 10.1038/353769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Parton R. G., Hauri H. P., Simons K., Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M. I., Mayorga L. S., Casey P. J., Stahl P. D. Evidence of a role for heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins in endosome fusion. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1695–1697. doi: 10.1126/science.1348148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. C., Kawata M., Yoshida Y., Takai Y., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. C terminus of the small GTP-binding protein smg p25A contains two geranylgeranylated cysteine residues and a methyl ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorvel J. P., Chavrier P., Zerial M., Gruenberg J. rab5 controls early endosome fusion in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90316-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Cox A. D., Hisaka M. M., Graham S. M., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Isoprenoid addition to Ras protein is the critical modification for its membrane association and transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6403–6407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Lutz R. J., Cox A. D., Conroy L., Bourne J. R., Sinensky M., Balch W. E., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Isoprenoid modification of rab proteins terminating in CC or CXC motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6264–6268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella B. T., Maltese W. A. rab GTP-binding proteins implicated in vesicular transport are isoprenylated in vitro at cysteines within a novel carboxyl-terminal motif. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8540–8544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella B. T., Maltese W. A. rab GTP-binding proteins with three different carboxyl-terminal cysteine motifs are modified in vivo by 20-carbon isoprenoids. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3940–3945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard J. M., Kahn R. A., Stahl P. D. Evidence for ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) as a regulator of in vitro endosome-endosome fusion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):13047–13052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Stahl P. D. Structure-function relationship of the small GTPase rab5. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24475–24480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Pang I. H., Duronio R. J., Gordon J. I., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Lipid modifications of G protein subunits. Myristoylation of Go alpha increases its affinity for beta gamma. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4654–4659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayorga L. S., Diaz R., Stahl P. D. Regulatory role for GTP-binding proteins in endocytosis. Science. 1989 Jun 23;244(4911):1475–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.2499930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moores S. L., Schaber M. D., Mosser S. D., Rands E., O'Hara M. B., Garsky V. M., Marshall M. S., Pompliano D. L., Gibbs J. B. Sequence dependence of protein isoprenylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14603–14610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musha T., Kawata M., Takai Y. The geranylgeranyl moiety but not the methyl moiety of the smg-25A/rab3A protein is essential for the interactions with membrane and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9821–9825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Chavrier P., Nigg E. A., Zerial M. Isoprenylation of rab proteins on structurally distinct cysteine motifs. J Cell Sci. 1992 Aug;102(Pt 4):857–865. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.4.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R. GTP-binding proteins in intracellular transport. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;2(2):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90161-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Goldstein J. L., Seabra M. C., Casey P. J., Brown M. S. Inhibition of purified p21ras farnesyl:protein transferase by Cys-AAX tetrapeptides. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford J. C., Pan Y., Wessling-Resnick M. Prenylation of Rab5 is dependent on guanine nucleotide binding. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23773–23776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford J., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Gamma-subunits of G proteins, but not their alpha- or beta-subunits, are polyisoprenylated. Studies on post-translational modifications using in vitro translation with rabbit reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9570–9579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabra M. C., Brown M. S., Slaughter C. A., Südhof T. C., Goldstein J. L. Purification of component A of Rab geranylgeranyl transferase: possible identity with the choroideremia gene product. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1049–1057. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90253-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Lutz R. J. The prenylation of proteins. Bioessays. 1992 Jan;14(1):25–31. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Smith T. F. Pattern-induced multi-sequence alignment (PIMA) algorithm employing secondary structure-dependent gap penalties for use in comparative protein modelling. Protein Eng. 1992 Jan;5(1):35–41. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E. S., Melançon P., Howell K. E. Targeting and fusion in vesicular transport. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;2(12):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90051-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich O., Horiuchi H., Bucci C., Zerial M. Membrane association of Rab5 mediated by GDP-dissociation inhibitor and accompanied by GDP/GTP exchange. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):157–160. doi: 10.1038/368157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich O., Stenmark H., Alexandrov K., Huber L. A., Kaibuchi K., Sasaki T., Takai Y., Zerial M. Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor as a general regulator for the membrane association of rab proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18143–18150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valencia A., Chardin P., Wittinghofer A., Sander C. The ras protein family: evolutionary tree and role of conserved amino acids. Biochemistry. 1991 May 14;30(19):4637–4648. doi: 10.1021/bi00233a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M., Clark S. G., Levinson A. D. The oncogenic activation of human p21ras by a novel mechanism. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):649–652. doi: 10.1126/science.3487832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessling-Resnick M., Braell W. A. Characterization of the mechanism of endocytic vesicle fusion in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16751–16759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. L., Maltese W. A. Isoprenylation of Rab1B is impaired by mutations in its effector domain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14561–14564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahraoui A., Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. The human Rab genes encode a family of GTP-binding proteins related to yeast YPT1 and SEC4 products involved in secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12394–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]