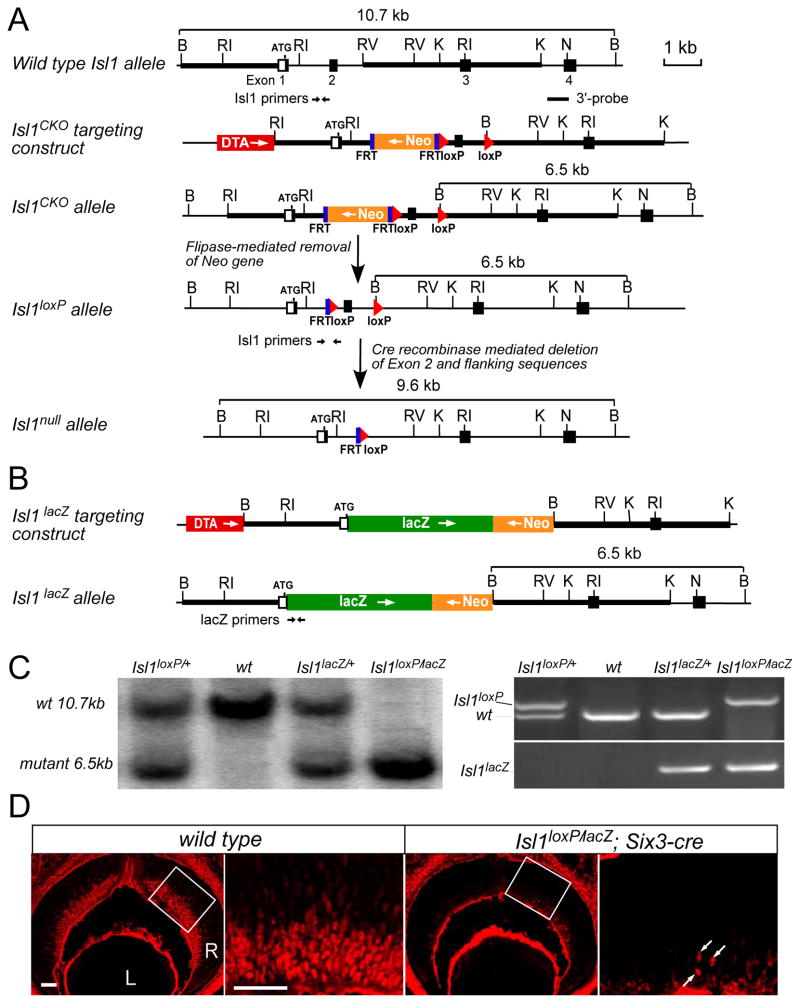
Figure 2.
Generation of Isl1 conditional knockout and Isl1-lacZ knock-in alleles. (A) Generation of Isl1 conditional allele. Isl1 genomic structure and restriction enzyme map is shown at the top. Open boxes are the non-coding exon sequences and filled boxes the coding sequences. Thick bars are the sequences used to generate the homologous arms in the targeting vector. The Isl1CKO targeting vector is made by inserting the FRT-flanked neomycin gene and the 5′ loxP sequence into Intron 1. The 3′ loxP sequence is inserted at the EcoRV site at Intron 2 and the EcoRV site is changed to BamHI site. ROSA26-FLPe mice are used to remove the neomycin resistance gene and generate Isl1 conditional knockout allele (Isl1lox). Tissue-specific deletion of Isl1 in the retina (Isl1null) is achieved by crossing Isl1lox mice to Six3-cre deleter mice. (B) Generation of Isl1lacZ knock-in allele. The DNA fragment containing reporter lacZ and neomycin resistance genes is used to replace the coding region of Exon 1, Exon2 and the flanking intron sequences in the targeting vector. Abbreviations: Neo, PGK-neomycin resistance gene; DTA, diphtheria toxin gene for negative selection of embryonic stem cells; lacZ, β-galactosidase reporter gene; FRT, flipase recognition sequence; loxP, Cre recombinase recognition sequence. Restriction enzymes: B, BamHI; RI, EcoRI; RV, EcoRV; K, KpnI; N, NotI. (C) Left panel, Southern genotyping confirmation of Isl1lacZ and Isl1lox mice using 3′ probe and BamHI digestion. Right panel, PCR genotyping using primers indicated in A&B can distinguish Isl1lox, Isl1lacZ, and wild type allele. (D) Anti-ISL1 immumolabeling of E13.5 retina sections confirms the deletion of ISL1 in the retina of Isl1loxP/lacZ; Six3-Cre mice. The enlarged views of the corresponding boxed regions are showed on the right. Deletion efficiency is greater than 90%. Arrows indicate residual ISL1 expression. Scale bar: 50 μm.