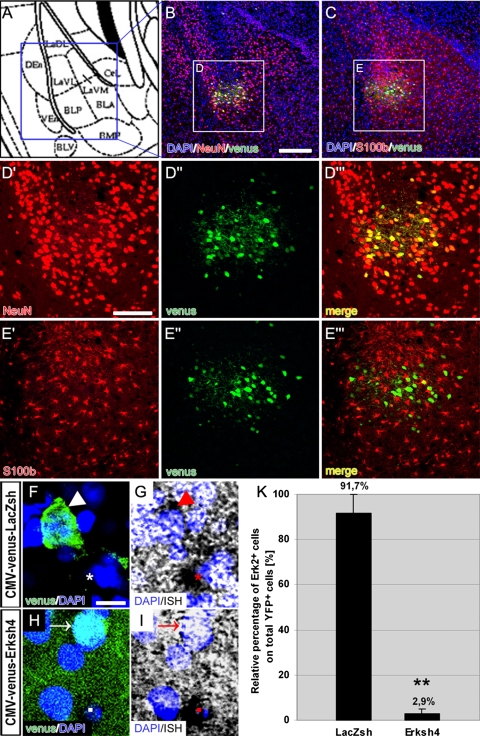
Fig. 3.
Tropism and downregulation efficiency of Erksh4 in vivo. a Schematic drawing of the amygdala at approximately −1.82 mm from bregma (according to (Franklin and Paxinos, 1997)). b, c Tropism of the virus. Representative photomicrographs of a portion of the LA (blue square in (a)) which show the site of injection, immunostained for YFP (green) and NeuN (red) (b) and for YFP (green) and S100β (red) (c); ounterstaining with DAPI (blue) shows the single-cell nuclei. (d′, d″, d′′′) Higher magnification of labeled cells (white square (D) in (b)) to show the single signals for NeuN (d′) and venus (d″) and the yellow color of their “merge” (D′′′) which highlights their co-localization; (e′, e″, e′′′) higher magnification of labeled cells (white square (E) in (c)) to show the single signals for S100 β (e′) and venus (e″): in contrast with (d′′′), their “merge” (e′′′) shows only a faint co-localization of the two signals (f, g, h, i). Downregulation of Erk2 mRNA. Higher magnification of labeled cells showing the specificity of downregulation in YFP+ cells infected with the Erksh4 virus (h, i) in comparison to YFP+ cells infected with the control virus (f, g): in (f, g) a clear ISH signal for Erk2 mRNA is visible in control infected cells (arrow heads), as high as in YFP− neighboring cells (asterisks); while in (h, i) the ISH signal is absent from YFP+ cells (arrows), although still present in neighboring YFP− cells (squares). k Double positive cells for YFP and Erk2 mRNA were counted in randomly selected sections from the amygdala of the four injected animals (n = 2 for each virus, bilaterally injected). The number of YFP+, Erk2+ cells was compared to the number of only YFP+ cells. As shown in the figure, in the control injected animals (LacZsh), the relative number of Erk2+ cells was not significantly different from the only YFP+, while in the Erksh4 injected brains, this number was significantly reduced (ANOVA; ** P ≤ 0.01), indicating an efficient downregulation of Erk2 also in vivo. Scale bars = 125 μm in (b, c); 60 μm in D–d’’’ and E–e’’’; 10 μm in (f, g, h, i)