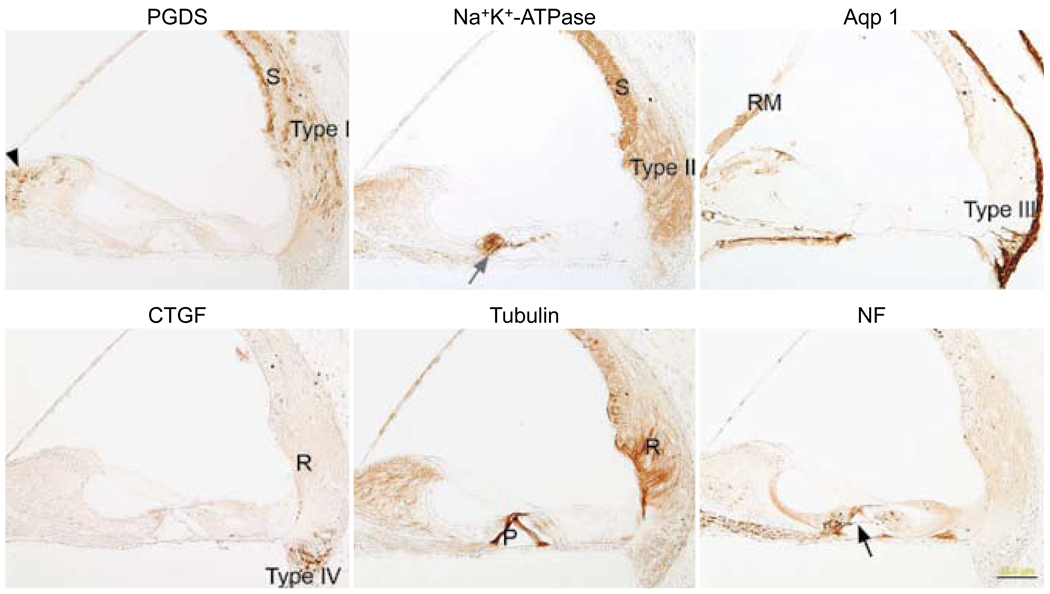
Fig. 5.
Celloidin removal with methanol saturated with sodium hydroxide followed by immunostaining. Successful immunostaining for all six antibodies is possible when methanol saturated with sodium hydroxide is used. Each antibody shows selectivity for appropriate cells (compare to Fig 1), and there is very little background. PGDS staining is evident in marginal and basal cells of stria vascularis (S), type I fibrocytes of spiral ligament (type I), and fibrocytes of spiral limbus (black arrowhead). Staining for Na+,K+-ATPase is evident in stria vascularis (S), type II fibrocytes of spiral ligament (type II), and nerve fibers below inner and outer hair cells (gray arrow). Aquaporin 1 antibody stains type III fibrocytes of spiral ligament (type III), medial portion of Reissner’s membrane (RM), cells lining bone of scala tympani, and some cells in spiral limbus. CTGF antibody stains type IV fibrocytes of spiral ligament (type IV). Antibody against tubulin stains pillar cells (P), root cells (R), and spiral limbus. Neurofilament antibody stains nerve fibers in osseous spiral lamina, nerve fibers below inner hair cell, tunnel crossing fibers (black arrow), and nerve fibers below outer hair cells. Calibration bar — 50 µm.