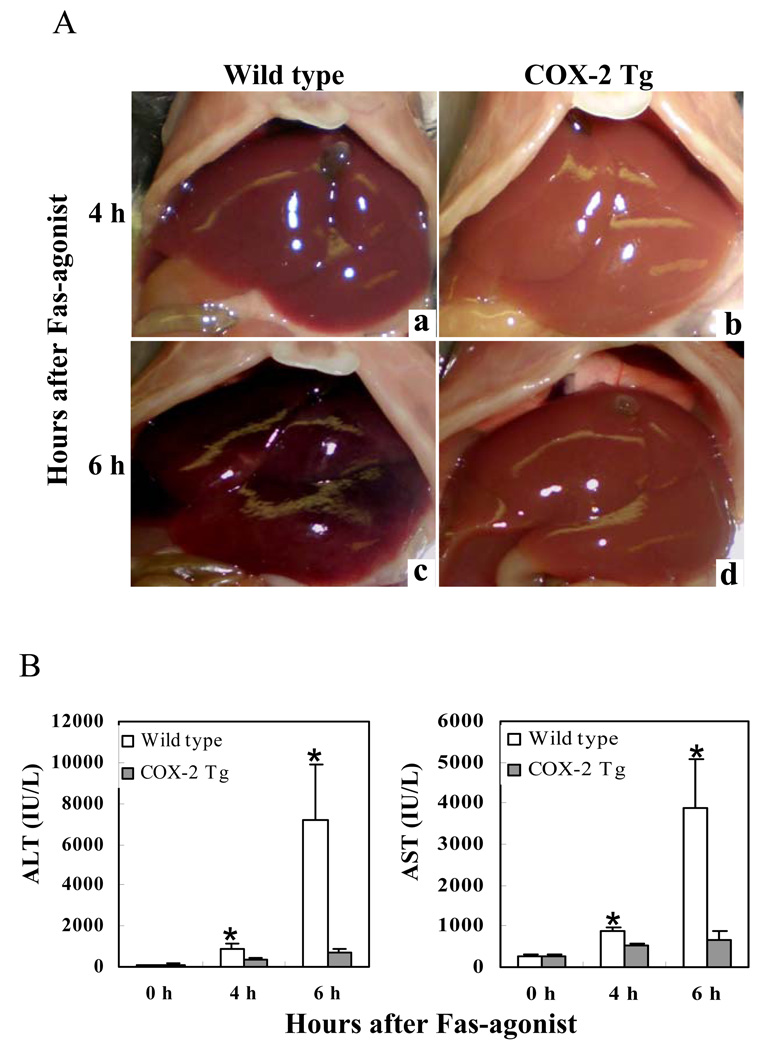
Figure 1. Hepatic overexpression of COX-2 prevents Fas-induced liver injury.
The COX-2 transgenic (Tg) mice and their age/sex-matched wild type mice were injected intraperitoneally with a single dose of purified hamster anti-mouse Fas monoclonal antibody Jo2 (0.5 µg/g body weight) to induce hepatocyte apoptosis. The animals were sacrificed at 4 hours and 6 hours after injection. The experiments include 6 mice per group. (A) Gross photographs of liver taken 4 hours (a and b) and 6 hours (c and d) after Jo2 injection. Note the livers of wild type mice turned to dark red after Jo2 injection because of massive hepatic hemorrhage, which was observed at 4 hour (a) and became much more prominent at 6 h (c). In contrast, the livers of COX-2 transgenic mice were completely normal at 4 h (b) and became slightly red at 6 h (d). (B) Serum levels of ALT and AST at 4 h and 6 h after Jo2 injection. Blood samples were collected and sera were separated for transaminase analysis. The COX-2 Tg mice show significantly lower serum ALT and AST levels than the wild type mice after Jo2 treatment. The data are expressed as mean ±SD from 6 mice (*p<0.01 vs. corresponding COX-2 Tg mice, Student’s t test).