Figure 3.
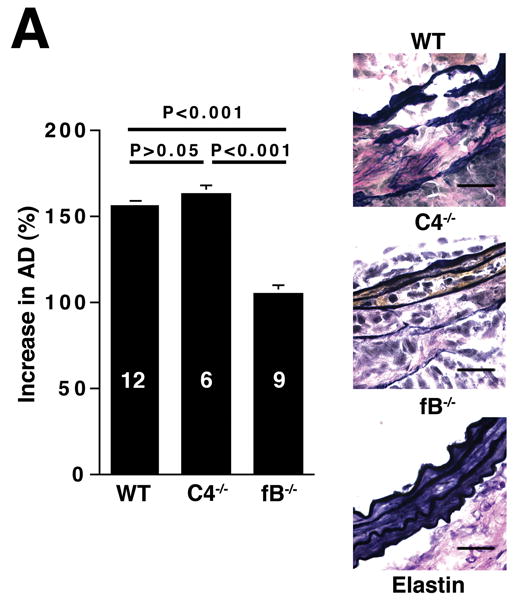
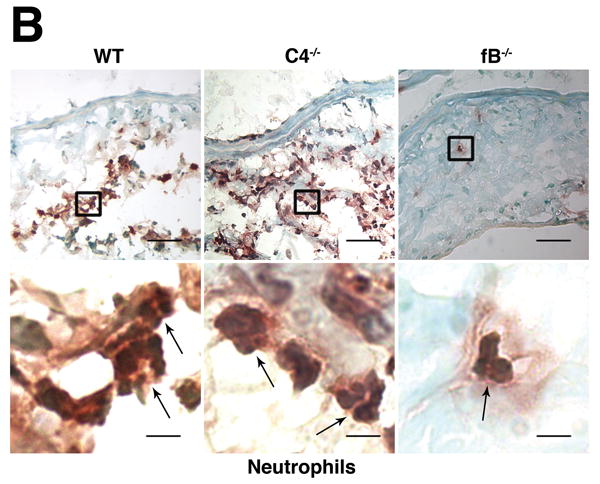
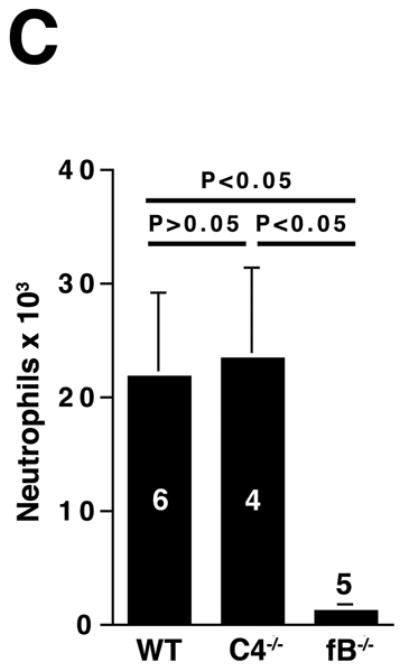
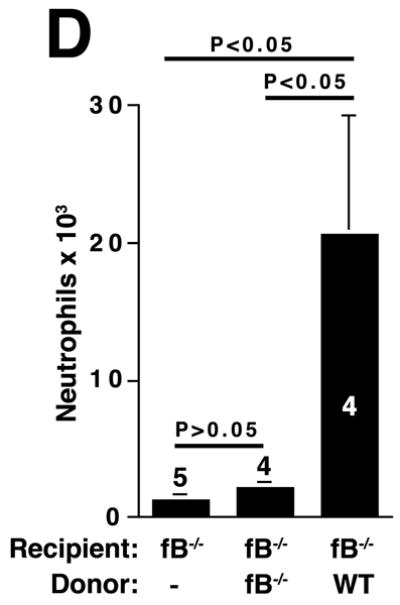
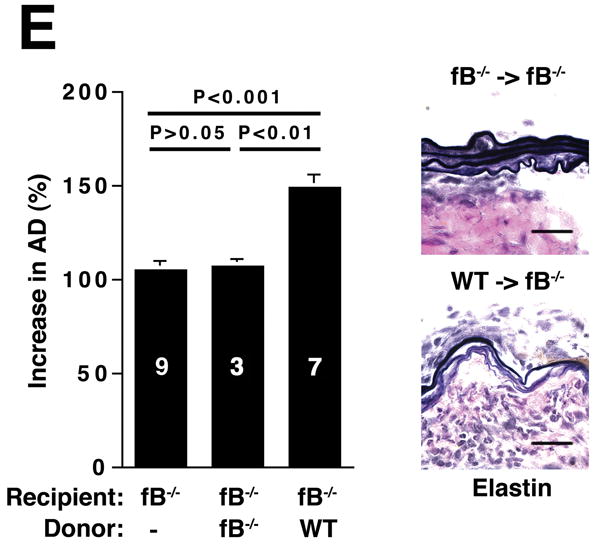
The alternative pathway is essential for AAA development. A) AD increase in WT, C4-/-, and fB-/- mice on day 14. VVG staining showed intact elastic fibers in fB-/- mice. Scale bar, 0.02 mm. B) Neutrophils in aortic wall were stained with Gr-1 (brown) and identified by their segmented nuclei (arrows). Insets from upper panels are shown at higher magnification in lower panels. Scale bar, 0.025 mm (upper panels), 0.01 mm (lower panels). C) The absolute number of neutrophils was calculated by multiplying the total number of cells per aorta by the percentage of CD45+/Gr-1+ cells. D) 24 h following the last WT or fB-/- serum injection, aortas were harvested and the number of neutrophils per aorta was calculated (D). Another group of mice were sacrificed on day 14 and the AD was assessed (E). Reconstitution with WT sera led to AAA development and fragmentation of elastic fibers in fB-/- mice. Scale bar, 0.02 mm. The number of animals per genotype is indicated for each group.
