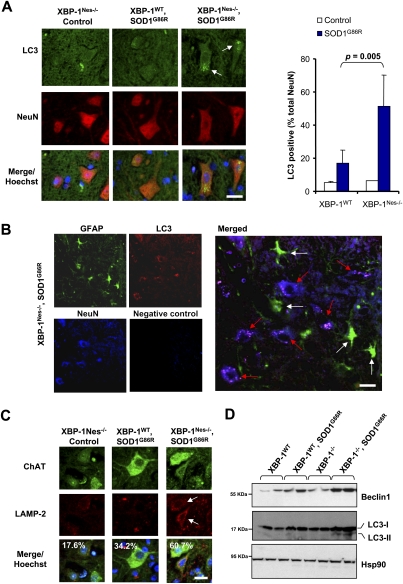
Figure 6.
XBP-1 deficiency increases autophagy levels in neurons of SOD1G86R transgenic mice. (A) Autophagosomes were directly observed in the spinal cord of control of mSOD1G86R transgenic mice on an XBP-1WT or XBP-1Nes−/− background by inmunofluorescence using an anti-LC3 antibody (green). Neurons were costained with an anti-NeuN antibody (red) and with Hoechst (nucleus, blue). Images are representative of the analysis of five different animals per group of ∼125–130 d of age. (Right panel) Quantification of the percentage of NeuN-positive cells containing LC3-positive vacuoles. Values represent average and standard deviation. P-value was calculated using Student's t-test. Bar, 10 μm. (B) The colocalization between LC3-positive dots (red) with neurons (NeuN, blue) or astrocytes (GFAP, green) was analyzed in the spinal cord of a mSOD1G86R transgenic mice using coimmunofluorescence. A merged picture is presented where white arrows indicate astrocytes and red arrows indicate neurons. A negative control of staining without primary antibodies is presented. Bar, 20 μm. (C) Lysosomes were visualized in the samples in A after LAMP-2 staining (red). Colocalization with motoneurons was evaluated after ChAT (green) staining (white arrow). Total cells were stained with Hoechst (nucleus, blue). Quantification of LAMP-2-positive motoneurons is indicated in the inset. Bar, 20 μm. (D) Beclin-1, LC3, and Hsp90 expression were determined in spinal cord protein extracts from symptomatic mSOD1G86R transgenic or control mice by Western blot. LC3-II form is indicated. Two representative animals are shown per group.