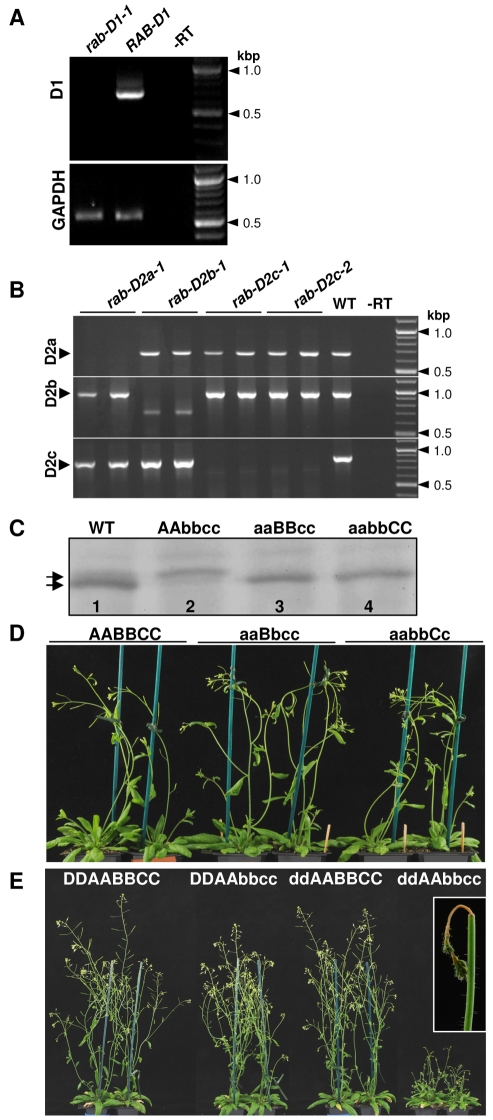
Fig. 6.
Phenotypes of insertional mutants in the Rab-D1 and Rab-D2 subclasses. (A,B) RT-PCR analysis of Rab-D1 and Rab-D2 transcript abundance in plants carrying insertion mutants in individual genes or in wild-type plants (WT). –RT indicates PCR without reverse transcription on RNA isolated from wild-type plants. Transcripts for GAPDH served as a loading control. (C-E) Genotypes are indicated by the letters D, A, B and C denoting RAB-D1, RAB-D2a, RAB-D2b and RAB-D2c, respectively. Lower case letters (d, a, b, c) denote a mutant allele. (C) Immunoblot analysis of protein extracts from whole seedlings and T-DNA insertion mutants using a peptide antibody that recognises a conserved epitope in the Rab-D2 subclass. Extracts were prepared from wild-type plants and three double mutant genotypes that retained only a single wild-type RAB-D2 locus: lane 2, genotype AAbbcc retains only RAB-D2a; lane 3, genotype aaBBcc, retains only RAB-D2b; lane 4, genotype aabbCC retains only RAB-D2c. In the wild type (lane 1), the antibody recognises two RAB-D2-specific bands (arrows), with the upper band corresponding to RAB-D2a and the stronger lower band corresponding to RAB-D2b and RAB-D2c. (D) Phenotype of wild-type plants (AABBCC) or plants carrying a single wild-type copy of a single Rab-D2 gene, either RAB-D2b (aaBbcc) or RAB-D2c (aabbCc). (E) Phenotype of wild-type plants (DDAABBCC) or plants carrying mutations either in RAB-D1 (ddAABBCC) or in RAB-D2b and RAB-D2c (DDAAbbcc), or in all three loci (ddAAbbcc).