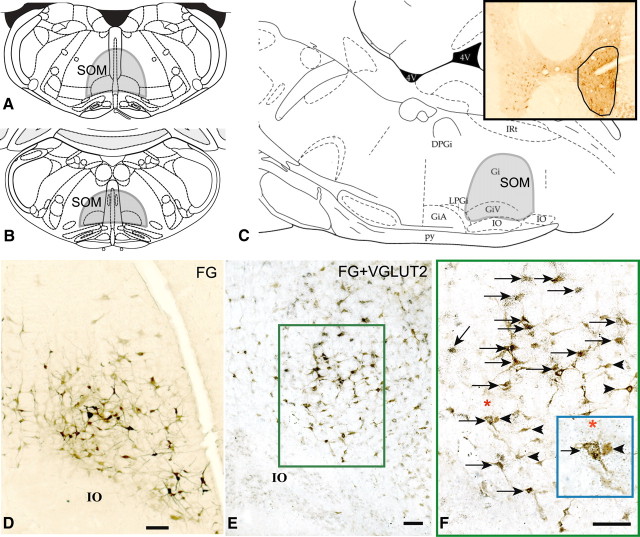
Figure 1.
A–C, Coronal sections (A, B) and sagittal section (C) from the rat atlas of Paxinos and Watson (2005) showing the extent of the SOM (shaded area); the SOM region included the GiV and medullary gigantocellular reticular nucleus (Gi), nucleus paramedianus, and nucleus raphe obscurus that lies immediately dorsal to GiV. Inset in C shows the FG injection site in the ventral horn of the spinal cord at C8–T1 level. D, Retrogradely labeled (FG-immunoreactive) neurons (brown) within the SOM after spinal ventral horn injections of FG; E, double-labeling of FG-ir neurons (brown) for the presence of VGLUT2 mRNA showed that an average of 61% of FG-immunoreactive neurons also contained VGLUT2 mRNA (black puncta) thus marking them as glutamatergic. F, High power photomicrograph of the boxed region in E. Arrows indicate double-labeled (FG and VGLUT2) neurons in the SOM and arrowheads indicate single-labeled (FG) neurons. Inset in F shows enlarged view of two neurons underneath the asterisk—one single-labeled (FG) and one double-labeled (FG and VGLUT2). GiA, Gigantocellular reticular nucleus, α part; IO, inferior olive; py, pyramidal tract; IRt, intermediate reticular nucleus. Scale bars: D–F, 100 μm.