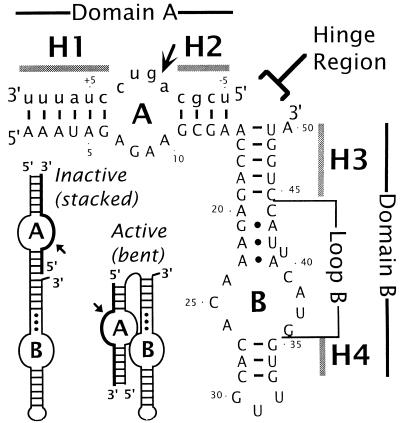
Figure 1.
Postulated secondary structure of the complex between the hairpin ribozyme and its cognate substrate. Ribozyme and substrate sequences are in uppercase and lowercase type, respectively. Ribozyme nucleotides are numbered from 1 to 50. Substrate nucleotides are numbered with negative numbers 5′ to the cleavage site and positive numbers 3′ to the cleavage site. A short arrow indicates the cleavage-ligation site. The four helical domains are designated as H1–H4, and the two internal loops as A and B. Proposed noncanonical base pairs at the top of loop B (22) are indicated with dots. Domain A is defined as the helical element comprising H1, loop A, and H2. Similarly, domain B stands for the H3-loop B-H4 element. Three base pairs (one in H1 and two in H2) of the naturally occurring sequences have been changed to minimize self-complementarity of the substrate (refs. 13 and 16; E. K. O’Neill, N.G.W., K. J. Hampel, J.E.H., and J.M.B., unpublished work). A rate-enhancing U39C mutation also was introduced. The putative hinge region is indicated. (Inset) Schematic cartoon showing the two proposed conformations of the hairpin ribozyme. See text for details.