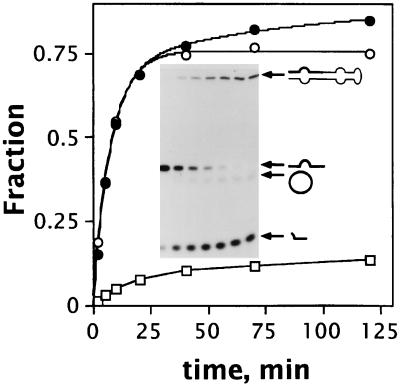
Figure 2.
Covalent trapping of the extended ribozyme-substrate complex with T4 RNA ligase. Substrate cleavage reactions were carried out either in the absence (•) or in the presence (○) of T4 RNA ligase (see Materials and Methods). Time courses were fitted to double- or single-exponential equations, respectively (see Materials and Methods). Amplitudes (A1 and A2) and rates (r1 and r2) for the biphasic reaction in the absence of RNA ligase were A1 = 0.71, r1 = 0.13 min−1; A2 = 0.19, r2 = 0.01 min−1. Parameters for the monophasic reaction in the presence of RNA ligase were A = 0.73, r = 0.12 min−1. The fraction of substrate ligated to the ribozyme when T4 RNA ligase was present is also shown (□). Reactions with or without RNA ligase were carried out side by side with the same ribozyme and substrate solutions. (Inset) Electrophoretic analysis of a cleavage reaction carried out with 5′-end labeled substrate in the presence of T4 RNA ligase. Lanes from left to right correspond to the data points in the graph. The migration positions of the substrate-ribozyme covalent complex, uncleaved substrate, circularized substrate, and 5′ cleavage product are shown from top to bottom. Substrate strands are depicted with a thicker line. The residual amount of circularized substrate is the result of an intramolecular ligation reaction catalyzed by T4 RNA ligase on free substrate molecules (23). A similar electrophoretic analysis was carried out in the absence of RNA ligase (not shown).