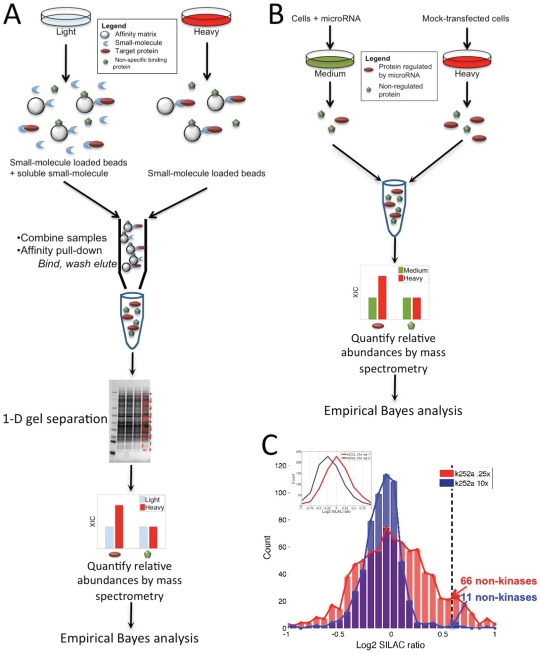
Figure 1. Schematics of SILAC-based experiments analyzed in our study.
(A) Small-molecule target identification workflow, as described in [30]. HeLa S3 cells were cultured in “heavy” medium, containing amino acids enriched in stable isotopes (13C and 15N), and “light” medium containing forms of natural isotope abundance. Both the heavy and light lysates were incubated with small-molecule loaded beads (referred to as the affinity matrix) while the light lysate contained the addition of a soluble form of the small-molecule that competed with the affinity matrix for binding to target proteins. The red ovals represent a target protein that was bound to all 3 small-molecule loaded beads shown in this schematic for the heavy lysate, but was competed off of 2 of the 3 beads in the light lysate. The green pentagons represent a protein that bound non-specifically to the beads in both the heavy and light lysates. Proteins bound to the affinity matrix were enriched by affinity pull-down, their relative abundances were quantified by LC-MS/MS, and targets were identified by analyzing the resulting abundance ratios, 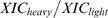 , using the empirical Bayes framework described in the text. (B) microRNA workflow, as described in [4]. HeLa cells were transfected with microRNAs or mock-transfected, and pulse-labeled after 8 hours with “medium” or “heavy” amino acid isotopes. After 24 hours, samples were combined and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The red ovals represent a protein regulated by the microRNA that was depleted in the medium lysate, and the green pentagons represent an unregulated protein of equal abundance in both lysates. (C) Two affinity pull-down experiments performed at different soluble competitor concentrations of the protein kinase inhibitor k252a displayed distinct variances of log2 SILAC ratio distributions. Applying a commonly used threshold of 1.5-fold (log2 threshold of .58) to identify significant proteins inferred 66 non-kinases (indicative of false-positives) for the high-variance experiment compared to 11 for the low-variance experiment, suggesting the necessity of experiment-specific models. (inset) The red curve represents the same k252a experiment, performed at .25x concentration, as displayed in the main plot, and the grey curve represents a replicate performed on the same cellular lysate with the same k252a concentration. This replicate experiment displayed a shift in the overall distribution due to non 1-to-1 mixing of heavy and light samples, which should be accounted for by appropriate normalization.
, using the empirical Bayes framework described in the text. (B) microRNA workflow, as described in [4]. HeLa cells were transfected with microRNAs or mock-transfected, and pulse-labeled after 8 hours with “medium” or “heavy” amino acid isotopes. After 24 hours, samples were combined and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The red ovals represent a protein regulated by the microRNA that was depleted in the medium lysate, and the green pentagons represent an unregulated protein of equal abundance in both lysates. (C) Two affinity pull-down experiments performed at different soluble competitor concentrations of the protein kinase inhibitor k252a displayed distinct variances of log2 SILAC ratio distributions. Applying a commonly used threshold of 1.5-fold (log2 threshold of .58) to identify significant proteins inferred 66 non-kinases (indicative of false-positives) for the high-variance experiment compared to 11 for the low-variance experiment, suggesting the necessity of experiment-specific models. (inset) The red curve represents the same k252a experiment, performed at .25x concentration, as displayed in the main plot, and the grey curve represents a replicate performed on the same cellular lysate with the same k252a concentration. This replicate experiment displayed a shift in the overall distribution due to non 1-to-1 mixing of heavy and light samples, which should be accounted for by appropriate normalization.